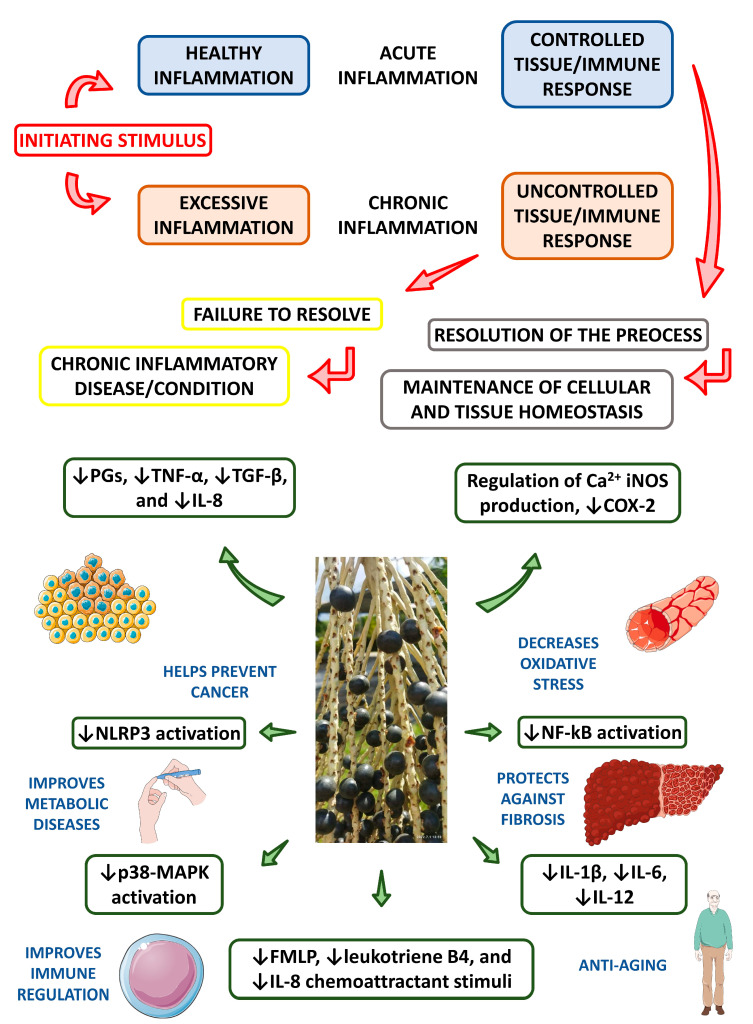
Figure 9.
Anti-inflammatory effects of açaí. Açaí improves anti-inflammatory status by directly reducing the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and expression of proinflammatory signaling pathways. Symbols and abbreviations: ↑: increase; ↓: decrease; Ca2+: calcium; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; FMLP: N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-8: interleukin-8; IL-12: interleukin-12; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; iNOS: inflammatory nitric oxide synthase; PGs: prostaglandins; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.