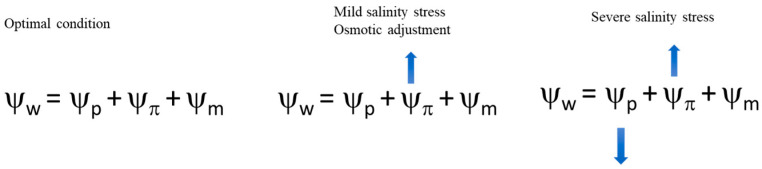
Figure 1.
Water balance of crops under normal conditions and under progressive stress conditions (from left to right). The increase in salinity stress induces the accumulation of osmolytes that increase the ability of root cells to uptake water (the cell osmotic potential becomes more negative). The progression of salinity and its severity cannot be counteracted with only osmolytes; the plant does not uptake water and loses its turgor. ΨW = water potential; Ψp = pressure potential; Ψπ = gravimetric potential; and Ψm = matric adsorption force.