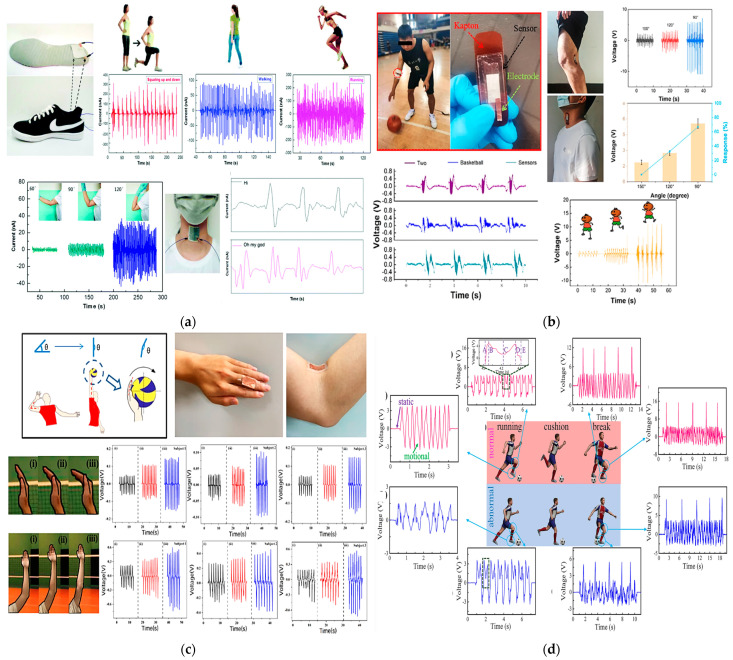
Figure 13.
Piezoelectric sensors: PVDF/BaTiO3-based sensor integrated into a sole with the corresponding output currents generated during squatting, walking, and running activities, elbow extension and flexion to 60°, 90°, and 120°, and the pronunciation of short sentences (a) [22]. PVDF/DMF-based sensor applied on an athlete’s elbow and the corresponding voltage signals generated at different bending angles and during different physical activities (b) [39]. A schematic diagram of different bending angles of the palm during the test of the PVDF sensor. The output piezoelectric voltages of three subjects when finger and elbow bending angle change are also reported (c) [42]. Soccer player motion monitoring test using the PVDF–HFP-based sensor (d). Pictures of a soccer players’ actions, showing normal ankle motion, abnormal ankle motion, normal knee motion, and abnormal knee motion. Moreover, the “brake” action of the same motion is also monitored and reported [64].