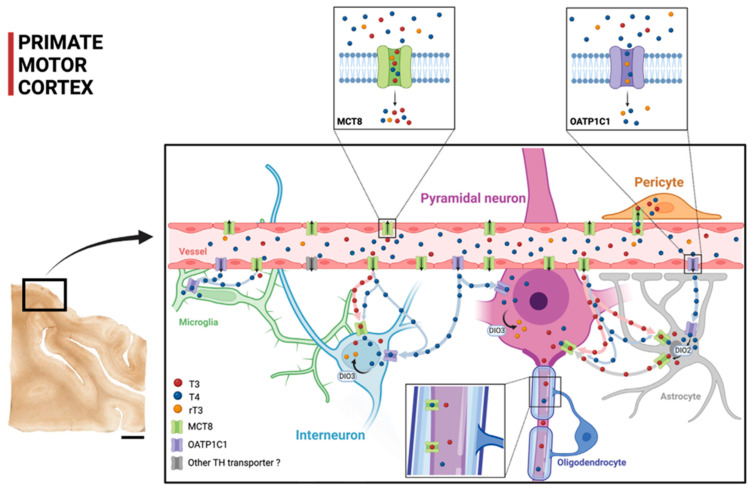
Figure 9.
Model of TH transport in human and primate motor cortex based on our contribution. The two small frames above show the TH transport affinities for MCT8 and OATP1C1, with MCT8 facilitating primarily the transport of T3 and T4 and OATP1C1 facilitating the transport of T4 and rT3 (see legend for color key). The scheme shows the distribution of the transporters MCT8 and OATP1C1 and the possible flow of T3 and T4 in the human and non-human primate motor cortical cells. Circulating T3 and T4 pass through the vascular endothelium to the brain parenchyma, relying primarily on MCT8 and on, to a much lesser extent, OATP1C1 and other transporters. Then, T3 and T4 are transported to the intracellular medium by MCT8 and/or OATP1C1 in different target neural cells. T3 enters into astrocytes and some interneurons and pyramidal cells (more abundantly in non-human primates). T4 is converted into T3 by astrocytic DIO2, providing additional T3 to nearby neural cells. DIO3 at the neuronal cell membrane catalyzes the conversion of T4 to rT3 and T3 to T2. T4 enters into neural cells, where it can be stored. DIO2: Deiodinase 2, DIO3: Deiodinase 3. Scale bar = 4000 μm (Created with BioRender.com).