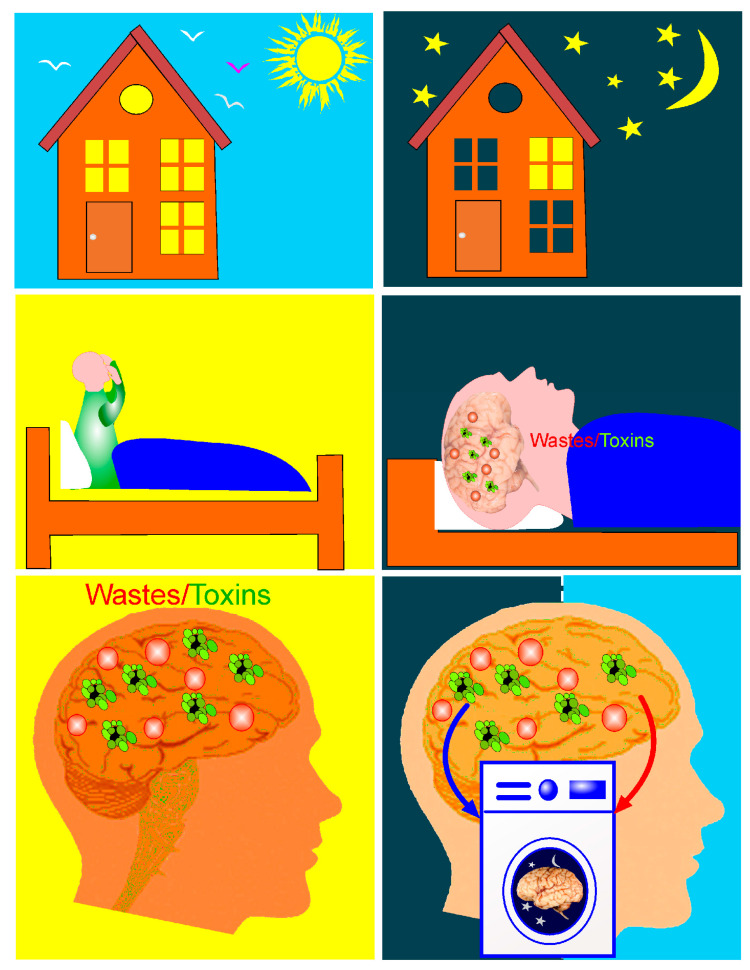
Figure 1.
BWRS activation during sleep. During wakefulness, the BWRS is inactive; therefore, wastes and toxins accumulate in the brain. During deep sleep, the BWRS is activated, which is accompanied by an increase in the drainage of brain tissues and the intense elimination of wastes and toxins. Figuratively speaking, the brain, during deep sleep, turns into a washing machine, removing unnecessary compounds from its tissues.