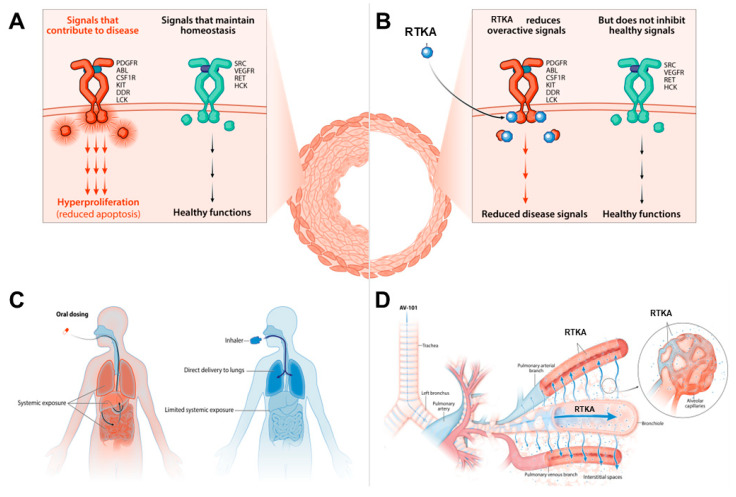
Figure 3.
Tyrosine kinase receptor signaling. (A). Upregulation of the tyrosine kinase receptor PDGFR and its ligand, platelet-derived growth factor, which is the most potent mitogenic for vascular smooth muscle cells, has been observed in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Ligand binding of platelet-derived growth factor induces dimerization of the receptors followed by activation by autophosphorylation and downstream signaling and transcription of pro-proliferative genes. This leads to excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in the arteriolar media and myofibroblasts in the vessel lumen, with media hypertrophy and intimal fibrosis. CSFIR and c-KIT are two additional PDGFR-related kinases that have also been involved in the pathobiology of PAH. CSF1R is expressed on monocytes and macrophages, which secrete platelet-derived growth factor ligands and inflammatory cytokines, promoting inflammation and remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature. C-KIT is expressed on endothelial progenitor cells and mast cells, and it is thought to play a role in perivascular inflammation and vascular remodeling. (B). RTKA reduce the upregulation of the pro-proliferative tyrosine kinase receptor-dependent signaling pathways. The RTKA imatinib inhibits PDGFR, DDR, c-KIT, CSF1R and ABL. The RTKA seralutinib inhibits PDGFR, CSF1R, and c-KIT, and increases bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-2. (C). Oral (left) and inhaled (right) administration of RTKA. (D). The inhaled formulation of the RTKA delivers high concentrations of the compound throughout the airways that reaches the pulmonary vasculature and the surrounding tissues to exert their anti-proliferative effects. ABL: abelson tyrosine kinase; CSF1R: colony stimulating factor 1 receptor; DDR: discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase; HCK: hematopoietic cell kinase; LCK: lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; RET: rearranged during transfection tyrosine kinase; RTKA: receptor tyrosine kinase antagonist; SRC: sarcoma tyrosine kinase; VEGFR: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.