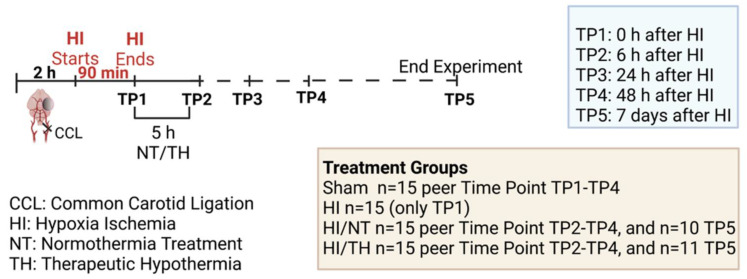
Figure 6.
Experimental design: 7-day-old rats (P7) were randomized according to sex and weight into four different treatment groups. Sham animals were not ligated and were only exposed to anesthesia for a short period of time (n = 15 animals per time point and condition). Common carotid ligation (CCL) was performed in the other groups, and animals were thereafter exposed to 90 min of hypoxia treatment (8% O2, 36 °C), resulting in moderate unilateral hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain injury. After hypoxia (time point 1—TP1, n = 15 animals), HI animals were sacrificed immediately after HI. Following HI, the remaining ligated animals were treated with either normothermia treatment (NT) (37 °C) or hypothermia treatment (TH) (32 °C) for 5 h. Blood, spleen, bone marrow, and brains were isolated at different time points (immediately, 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h (n = 15 animals per time point and condition)) after HI. Animals from the last time point (seven days after HI) were sacrificed, and brain slices were stained with hematoxylin to measure the area loss after HI/NT (n = 10) or HI/TH treatment (n = 11). Made using BioRender.com.