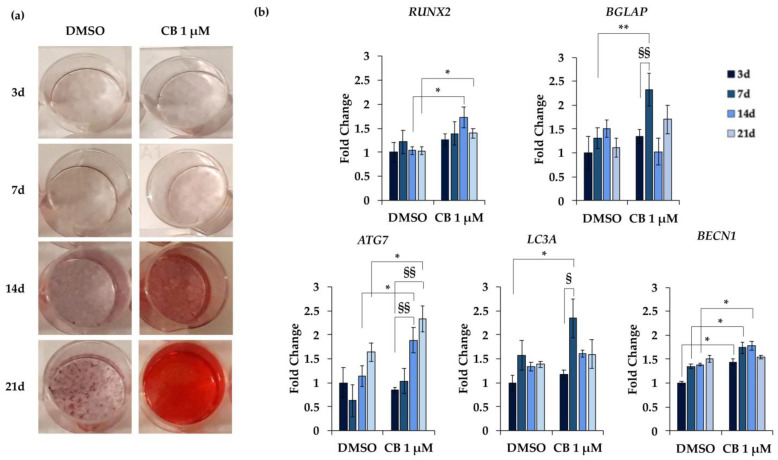
Figure 12.
Alizarin Red S staining and gene expression in human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells (hWJ-MSCs) during osteogenic differentiation. hWJ-MSCs were cultured in osteogenic medium for 3, 7, 14, and 21 days (d) and were treated with Cytochalasin B (CB) 1 μM or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 0.05% (CB vehicle). (a) Representative images of wells in which hWJ-MSCs were stained with Alizarin Red S. Osteogenesis was highlighted by the presence of the red calcium deposits. (b) Expression of RUNX2 (RUNX family transcription factor 2), BGLAP (bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein, also named osteocalcin), ATG7 (autophagy related 7), LC3A (microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3 alpha) and BECN1 (Beclin 1) genes was assessed. Data, obtained with real-time PCR, were normalized using three housekeeping genes (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase 1—HPRT1, TATA box binding protein—TBP and tyrosine 3 monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein zeta—YWHAZ); the normalized expression value of DMSO after 3 days from the beginning of the differentiation protocol was set up to 1, and all other gene expression values were reported to that sample. Data are reported as normalized fold change ± standard deviation (SD); n = 3. * p < 0.05 or ** p < 0.01 vs. DMSO-treated hWJ-MSCs at the same day; § p < 0.05 or §§ p < 0.01 vs. hWJ-MSCs treated with CB 1 μM at 3 days from the beginning of the osteogenic differentiation.