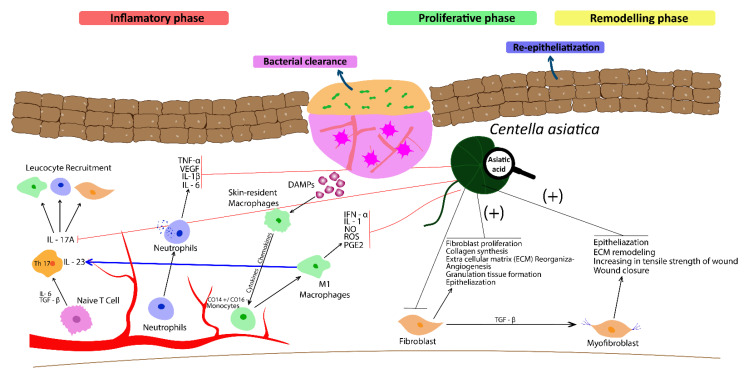
Figure 2.
Centella asiatica extract (CAE) and its bioactive constituent, asiatic acid (Aa) display a decrease in the wound area and faster healing by increasing collagen synthesis, and cellular proliferation, fibroblast division and re-epithelialization during proliferative and remodeling phases of wound healing. CAE and Aa also act in the inflammatory phase by inhibiting recruitment of immune defense cells, reducing synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and and IL-1β) and growth factors (TGF-β, PDGF and VEGF). Moreover, Aa inhibits the increase of serum levels of IL-17/IL-23. This figure was created with Adobe Illustrator.