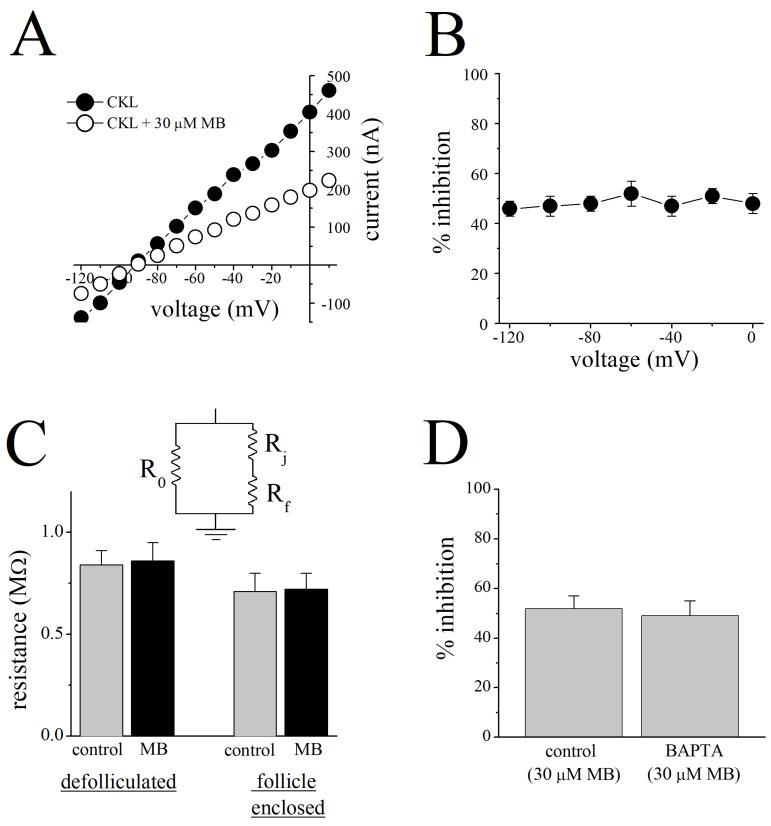
Figure 2.
Inhibition of cromakalim-induced K+ currents by MB is voltage-independent and not mediated through gap junctions. (A) Current-voltage relationship of cromakalim-activated currents recorded during 1 s voltage steps applied before (filled circles) and after application of 30 μM MB (open circles). (B) Different membrane potentials did not alter percentage inhibition of cromakalim-activated K+ currents by MB. Differences among the means of current inhibitions by 30 µM MB at different holding potentials were not statistically significant (p > 0.05, ANOVA, n = 5–7). (C) Inset to Figure 2C indicates the equivalent resistive-circuit diagram. The mean values for the sum of resistances through the oocyte gap junction (Rj), follicular cell membranes (Rf) in follicle-enclosed oocytes before (gray bars) and after 20 min administration of 30 μM MB (black bars) are shown on the right side (n = 14). Membrane resistance (Ro) of enzymatically defolliculated oocytes before and after MB treatment are presented on the left (n = 16). Values of resistances were calculated from current-voltage curves recorded in the range between –50 mV and +10 mV. (D) Effect of MB (30 μM) on cromakalim (100 μM)-induced K+ currents in control and in BAPTA-pretreated oocytes. CKL: cromakalim; MB: methylene blue.