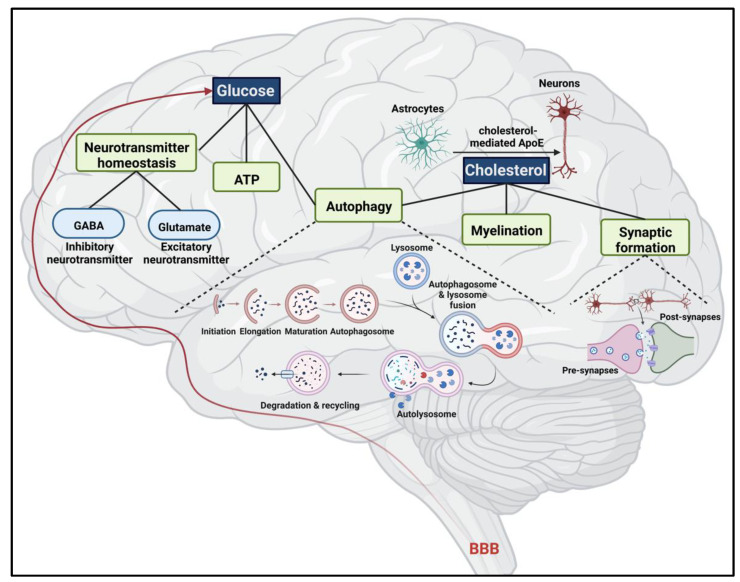
Figure 3.
Key roles of glucose and cholesterol in the brain. Glucose enters the brain through the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and is subsequently involved in ATP production, neurotransmitter homeostasis and autophagy activity. In the adult brain, cholesterol is mainly synthesized in the astrocytes and then delivered to neurons by transporter “ApoE”. In the brain, cholesterol greatly contributes to myelination, synaptic formation, and regulates autophagy. ApoE: apolipoprotein B; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; BBB: blood-brain barrier. GABA: gamma amino butyric acid. Information obtained from [119,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132]. Figure is created with BioRender.com.