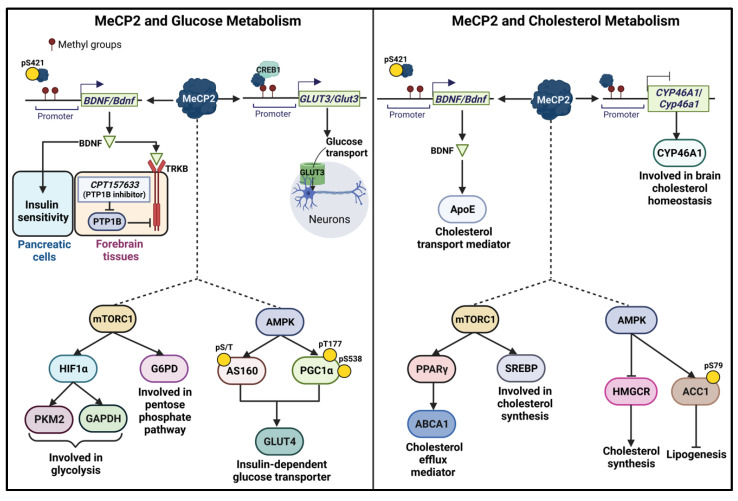
Figure 4.
The potential links between MeCP2 with glucose and cholesterol metabolism. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a downstream target of MeCP2, is engaged in both glucose and cholesterol metabolism; similar to mTORC1 and AMPK signaling pathways. Moreover, MeCP2 may regulate the expression of CYP46A1, which is a key factor in brain cholesterol homeostasis. MeCP2 promotes expression of GLUT3, which is a crucial transporter of glucose to neurons. ABCA1: ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1; ACC1: acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; AMPK: adenosine 5′-monophosphate activated protein kinase; AS160: Akt substrate of 160 kDa; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CREB1: cAMP response element-binding protein 1; CYP46A1: cytochrome P450 family 46 subfamily A member 1; G6PD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GLUT3: glucose transporter 3; GLUT4: glucose transporter 4; HIF1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase; MeCP2: methyl-CpG Binding Protein 2, mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; PGC-1α: peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha; PKM2: pyruvate kinase M2; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PTP1B: protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; SREBP: sterol regulatory element-binding protein, TRKB: tropomyosin receptor kinase B. Information obtained from [18,150,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183]. Please note that the molecular signaling cascades showing the link between MeCP2 and glucose metabolism as well as cholesterol metabolism were taken from different organs and cell type-specific regulation. Figure is created with BioRender.com.