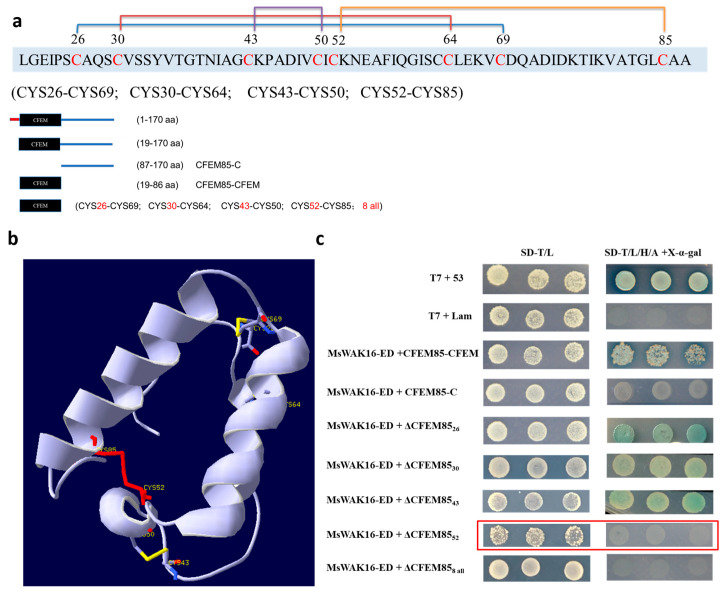
Figure 3.
Identification of the interaction site between MaCFEM5 and MsWAK16. (a) Schematic illustrations of MaCFEM85. Protein domains in MaCFEM85 were predicted and visualized using SMART (embl-heidelberg.de). (b) Positions of the eight cysteines in MaCFEM85 and a schematic showing the four disulfide bonds. (c) Truncated MaCFEM85 constructs were generated that included the CFEM domain (19–86 aa of the N-terminal, CFEM85-CFEM) and that included residues 87–170 without the CFEM domain (CFEM85-C). The other five variants were C26A(ΔCFEM8526), C30A(ΔCFEM8530), C43A(ΔCFEM8543), C52A(ΔCFEM8552), and C26/30/43/50/52/64/69/85A (ΔCFEM858 all). Each construct was co-transformed in yeast with MsWAK16-ED and grown on either the two-deficiency medium SD-T/L (SD-Trp/Leu) or the four-deficiency medium SD-T/L/H/A + X-α-gal (SD-Trp/Leu/His/Ade + X-α-gal).