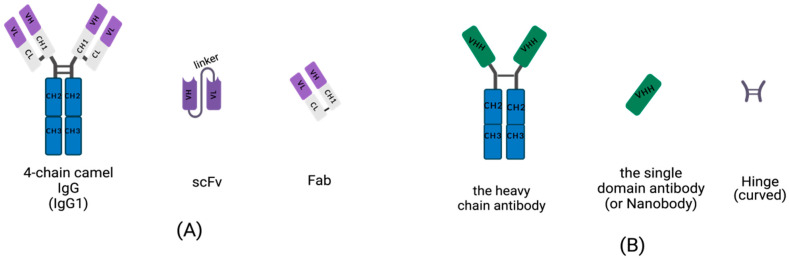
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for the primary structure of a conventional antibody, heavy-chain antibody (HCAb), nanobody, and small, recombinant antibody (This figure was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 27 March 2022). (A) A 4-chain camel IgG (IgG1), a class-conventional antibody in mammal serum, which consists of two light chains and two heavy-chains. The single light chain contains a variable region, VL, and a constant region, CL. The single heavy-chain contains a variable region, CL, and three constant regions, CH1, CH2 and CH3. The scFv is composed of a VH and VL pair-linked by an oligopeptide. A Fab fragment is formed by the first two domains of heavy-chain and light chain. (B) The single chain of HCAb contains two constant regions, CH2 and CH3 and a variable region, VHH, linked by curved hinge. VHH domain owns the smallest intact antigen-binding fragments, also known as single-domain antibodies (sdAbs) or nanobodies.