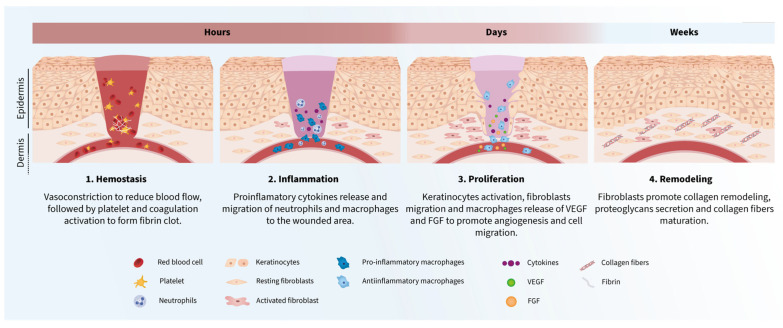
Figure 1.
Wound healing process phases. 1. Hemostasis. Rupture of the veins adjacent to the wound area, infiltration of platelets and erythrocytes that begin the processes of platelet aggregation and coagulation that culminate in the fibrin clot formation. Tissue damage causes the release of mediators, such as proinflammatory cytokines, that will promote cell migration in later phases. 2. Inflammation. Infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils is enhanced by proinflammatory mediators to face infection and moderate inflammation. 3. Proliferation. Activation and migration of several cell types as keratinocytes and fibroblasts promoting angiogenesis and re-epithelization. 4. Remodeling. Fibroblasts orchestrate the ECM modulation for tissue regeneration.