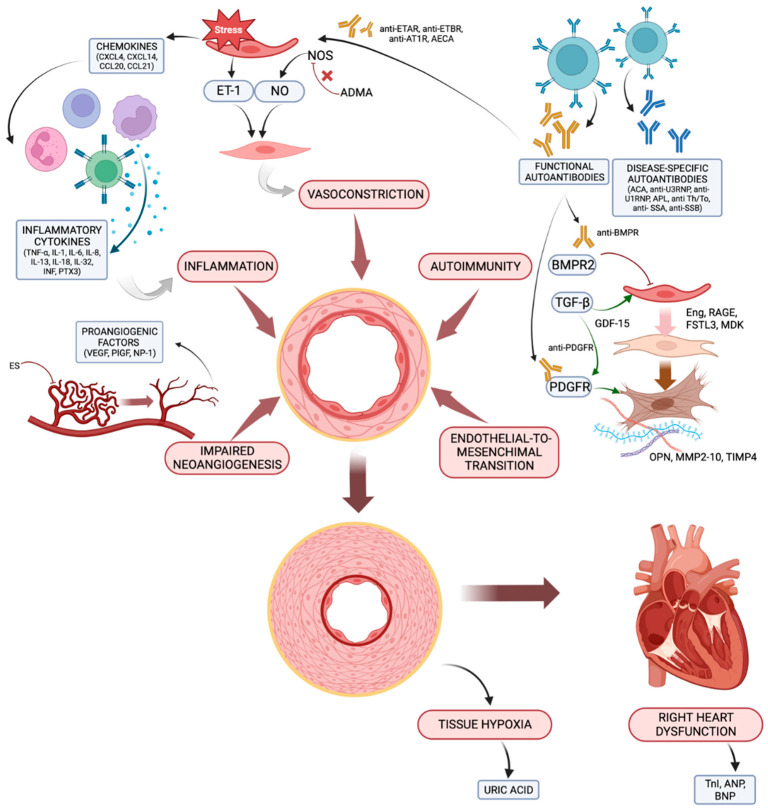
Figure 1.
The main pathogenetic mechanisms leading to CTD-PAH and the associated biomarkers. ACA, anti-centromere antibodies; ADMA, asymmetric dimethylarginine; AECA, anti-endothelial cells antibodies; aPL, antiphospholipid antibodies; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; AT1R, angiotensin receptor type 1; BMPR, bone morphogenic protein receptor; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; CCL, C-C motif ligand; CXCL, C-X-C motif ligand; Eng, endoglin; ES, endostatin; ET-1, endothelin-1; ETAR, endothelin receptor type A; ETBR, endothelin receptor type B; FSTL-3, follistatin-like 3; GDF-15, growth differentiation factor-15; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; MDK, midkine; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NO, nitric oxide; NP-1, neuropilin-1; OPN, osteopontin; PDGFR, placental derived growth factor receptor; PlGF, placental growth factor; PTX3, pentraxin 3; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; RNP, ribonucleoprotein; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TNF, TnI, troponin I; tumour necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Created with BioRender.com.