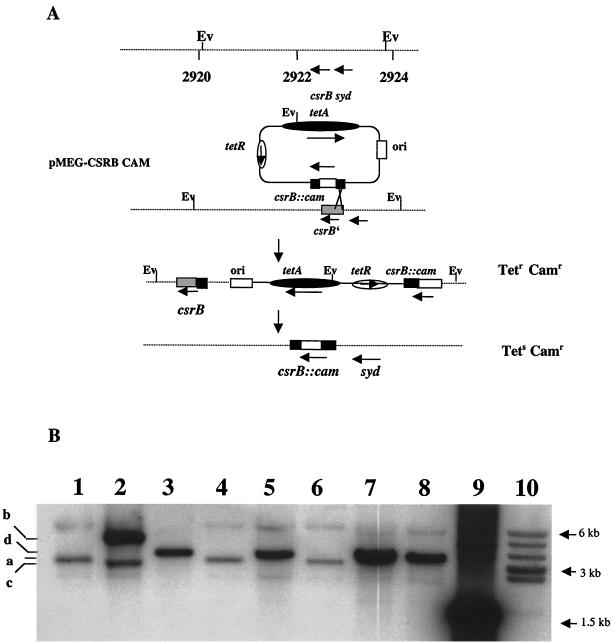
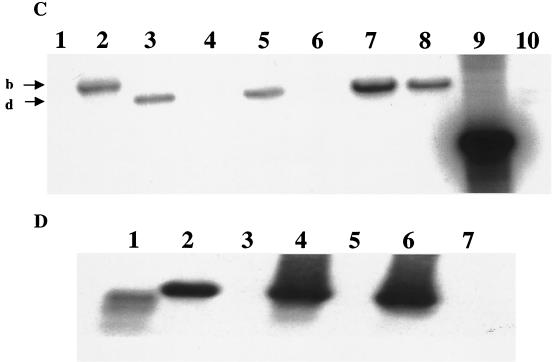
FIG. 2.
Construction and characterization of a csrB null mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy used for the replacement of the RNA-coding region of csrB, as described in Materials and Methods. Depicted are the chromosomal location of csrB, including the adjacent EcoRV (Ev) sites, the composition of the integration vector pMEG-CSRB-CAM, the structure of the integrant, and the final allelic replacement. Map coordinates are in kilobases (34). (B) Southern hybridization of csrB. Depicted are EcoRV-digested chromosomal DNA from the parental strain BW3414 (lane 1), the integrant RG-I9 BW3414 (lane 2), the first allelic replacement mutant RG1-B BW3414 (csrB::cam) (lane 3), MG1655 (lane 4), RG1-B MG1655 (csrB::cam) (lane 5), CAG 12079 (lane 6), RG1-B CAG12079-1 (csrB::cam) (lane 7), and RG1-B CAG 12079-2 (csrB::cam) (lane 8). Lanes 9 and 10 depict a csrB::cam-containing 1.5-kb BamHI-KpnI restriction fragment from pMEG-CSRB-CAM hybridized to the same probe and a prelabeled 1-kb DNA ladder, respectively. The identities of the hybridizing EcoRV restriction fragments from the csrB region of the parental strains (a), the integrant RGI-9 BW3414 (b and c), and the csrB::cam mutants (d) are indicated. (C) Reprobing of the chromosomal DNA. The blot shown in panel B was stripped and reprobed with a randomly labeled 0.88-kb cam marker from pMAK705. Note that DNA from parent strains fails to hybridize and that the fragments which hybridize to the cam probe are identical to fragments b and d of panel B. (D) Northern blot using a csrB riboprobe. Depicted are isolated csrB RNA (lane 1), total RNA from strains BW3414 (lane 2), RG1-B BW3414 (csrB::cam) (lane 3), MG1655 (lane 4), RG1-B MG1655 (csrB::cam) (lane 5), CAG12079 (lane 6), and RG1-B CAG12079-1 (csrB::cam) (lane 7).