Figure 3.
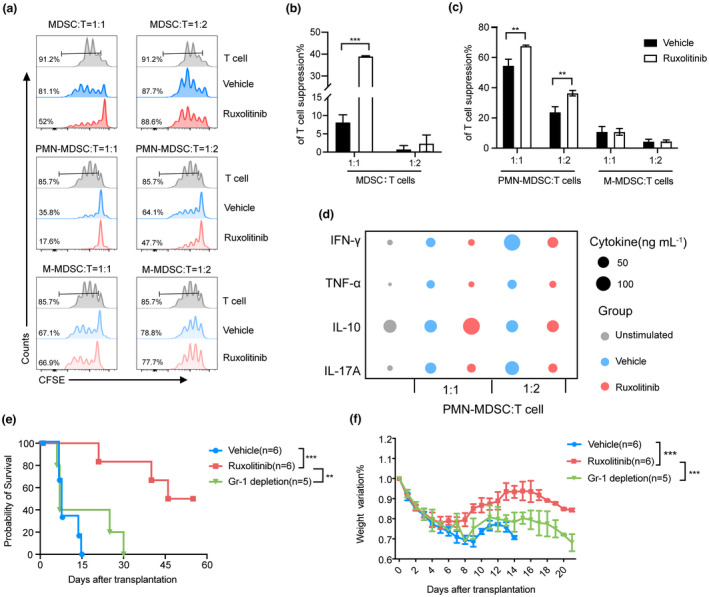
Ruxolitinib treatment enhanced immunosuppressive function of MDSCs, especially PMN‐MDSCs in aGVHD mice. Depletion of MDSCs exacerbated aGVHD lethality in ruxolitinib‐treated mice. (a–c) CFSE‐labelled CD3+ T cells (1 × 105 per well) from wild‐type C57BL/6 spleen were stimulated with CD3/28 beads and cocultured with different ratios of purified splenic MDSCs, PMN‐MDSCs and M‐MDSCs isolated from vehicle‐ and ruxolitinib‐treated mice at day 7 after transplantation for 72 h. Proliferation of CFSE‐labelled CD3+ T cells was measured with flow cytometry (Vehicle group, n = 3; Ruxolitinib group, n = 3). (d) The helper T cell‐related cytokines were detected in supernatants harvest from the above coculture system (n = 3). (e,f) aGVHD mouse models were built as described previously. Two hundred microgram anti‐Gr‐1 antibody was injected intraperitoneally into recipient mice with ruxolitinib treatment to deplete MDSCs as Gr‐1 depletion group from day 5 to day 29 every other day after transplantation. The overall survival and weight ratio were exhibited in each group (Vehicle group, n = 6; Ruxolitinib group, n = 6; Gr‐1 depletion group, n = 5). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) and from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
