Fig. 5. ResR activates whiB2 and clinical mutations lead to upregulation of whiB2.
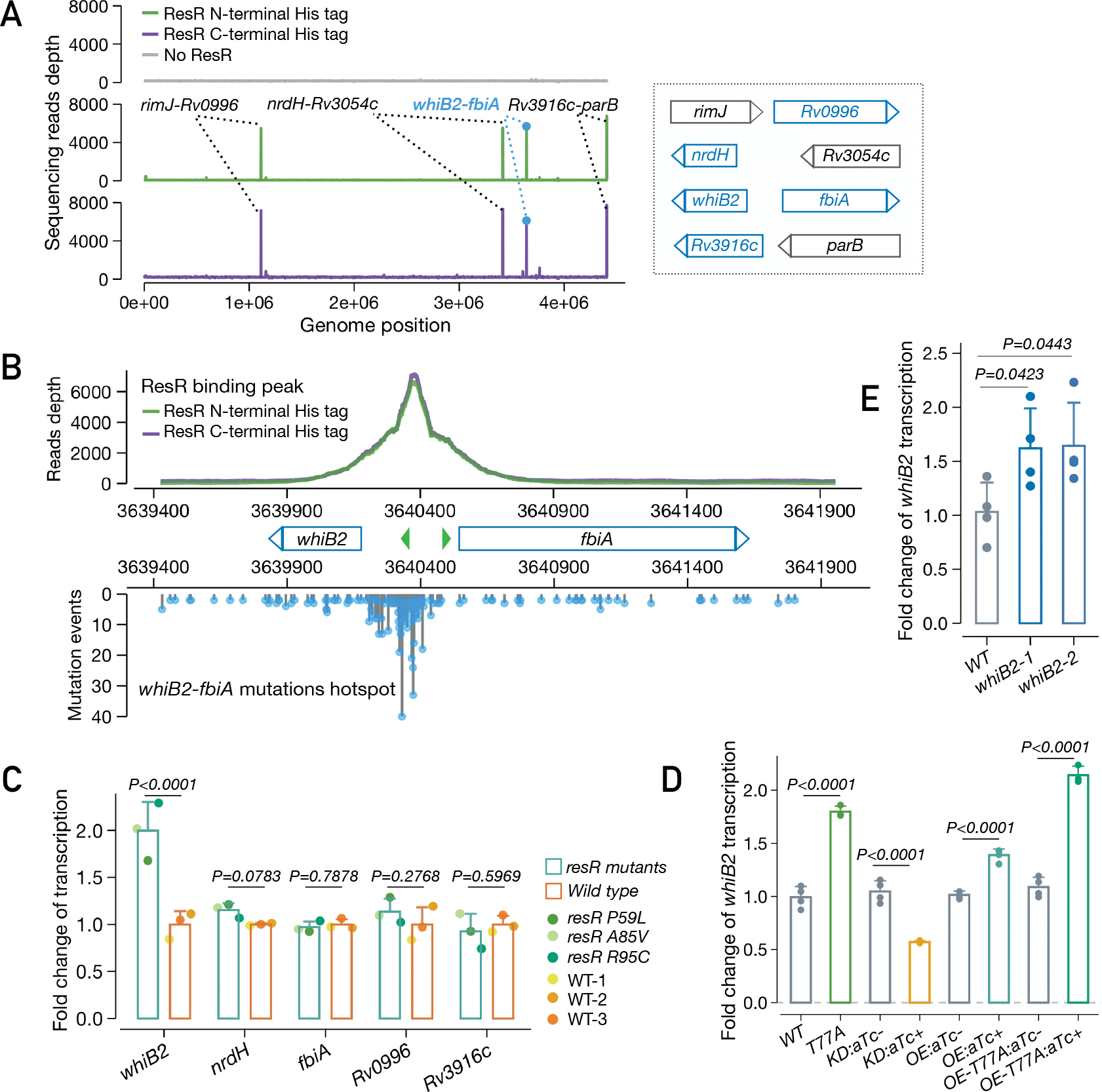
(A) IDAP-Seq identified binding sites of ResR. (B) ResR binding peaks overlaid with the mutations identified in clinical strains between whiB2-fbiA. The transcriptional start sites of whiB2 and fbiA are annotated (green arrows). (C) Ford change of transcription of putative ResR targets in resR mutants and wild-type strains, P values by the Wald test implemented in DEseq2. (D) Transcriptional changes of whiB2 in M. smegmatis strains: wild-type (WT), resR point mutant (T77A), CRISPR-i knock-down of resR (KD), merodiploid overexpression of wild-type resR (OE) or T77A mutant form (OE-T77A). The absence or presence of aTc was specified by (−) or (+), P values given by unpaired t test. (E) whiB2-fbiA mutant (3640375 C>T) exhibited upregulation of whiB2. whiB2–1 and whiB2–2 refer to the two parallel mutants, and P values given by unpaired t test.
