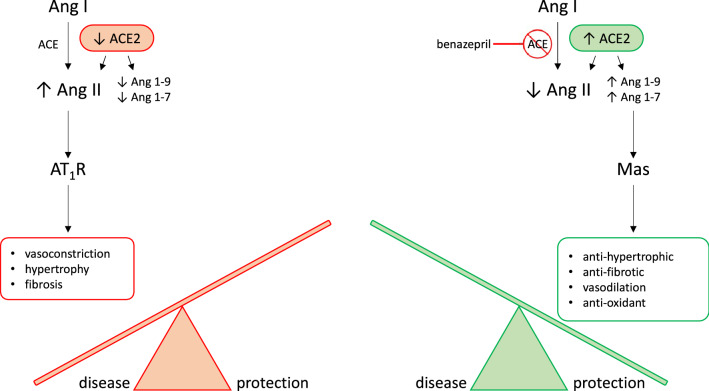
Figure 1.
Biological arms of the RAAS. RAAS activation is thought of as having two main pathways which act as counterregulatory mechanisms for one another. The classical RAAS pathway (in red orange) refers to the peptide cascade from angiotensin I (Ang I) to angiotensin II (Ang II) via ACE. This stimulates aldosterone production which then activates AT1 receptors (AT1R). Physiologic consequences of classical RAAS activation, including vasoconstriction, hypertrophy, and fibrosis, typical worsen congestive heart failure (CHF). Benazepril inhibits ACE, therefore activating the alternative RAAS pathway (in green). Activation of the alternative RAAS pathway is characterized by catalysis of Ang II to Ang1-7 by the enzyme ACE2. In turn, Ang1-7 activates Mas receptors leading to vasodilatation, diuresis, and natriuresis. These effects are protective against CHF. Our goal is to use mathematical modeling to determine a dosage which both reduces classical RAAS pathway activation and stimulates alternative RAAS pathway activation. This hypothetical dosage would maximize CHF-protective effects of benazepril.