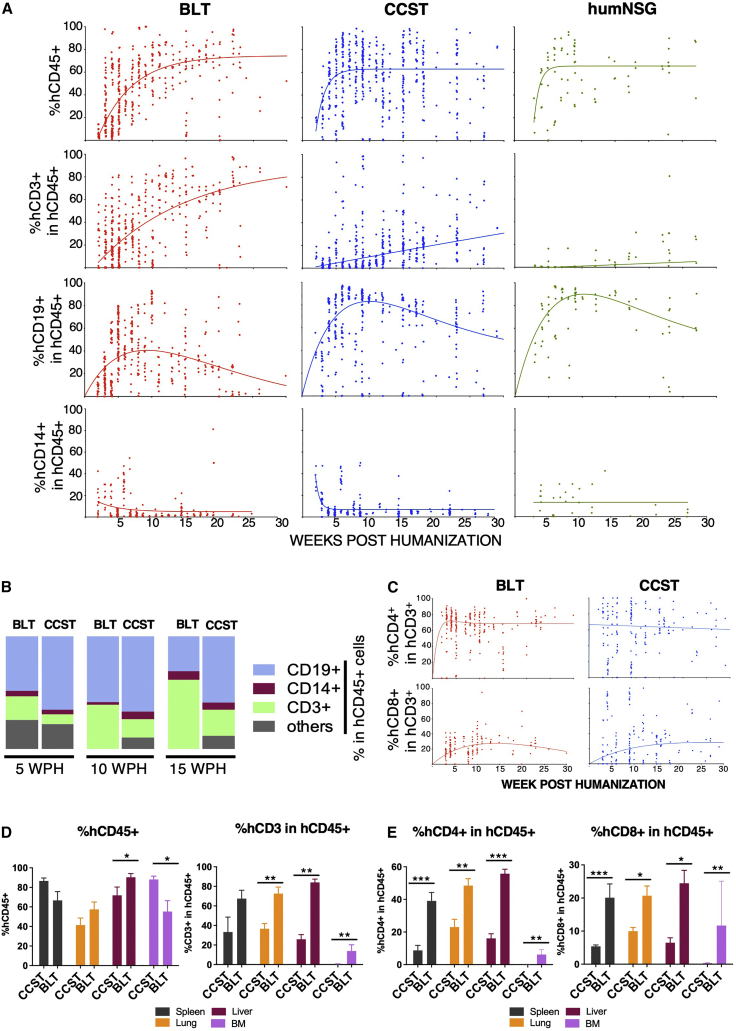
Figure 2.
Unlike humanized mice without a thymus (humNSG), CCST and BLT humanized models allow for robust T cell reconstitution
(A) Peripheral blood from mice of the three models was harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry for the level of human cell reconstitution (each dot represents a mouse analyzed at a given time point). Extent of the reconstitution of hCD45+ (calculated among total CD45+ cells [mouse and human]), hCD3+ (among hCD45+), hCD19+ (among hCD45+), and hCD14+ (among hCD45+) was as shown. A non-linear regression curve was calculated for each subpopulation using the growth exponential association model for all populations except hCD19, for which a two-phase exponential association model was applied.
(B) Graphic representation of the relative proportions of human T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+) and monocytic cells (CD14+) in BLT and CCST mice at 5, 10, and 15 weeks post humanization, showing an increase in T cell proportion over time for BLT mice.
(C) Dynamic changes in the level of human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells within the hCD3+ population in peripheral blood of CCST and BLT mice. Non-linear regression curves were calculated using a two-phase exponential association model.
(D and E) (D) Proportions of human CD45+ and CD3+ and (E) levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in tissues of CCST and BLT mice at 25 weeks post humanization as measured by flow cytometry. The Mann-Whitney test was applied to compare ranks of two groups. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.