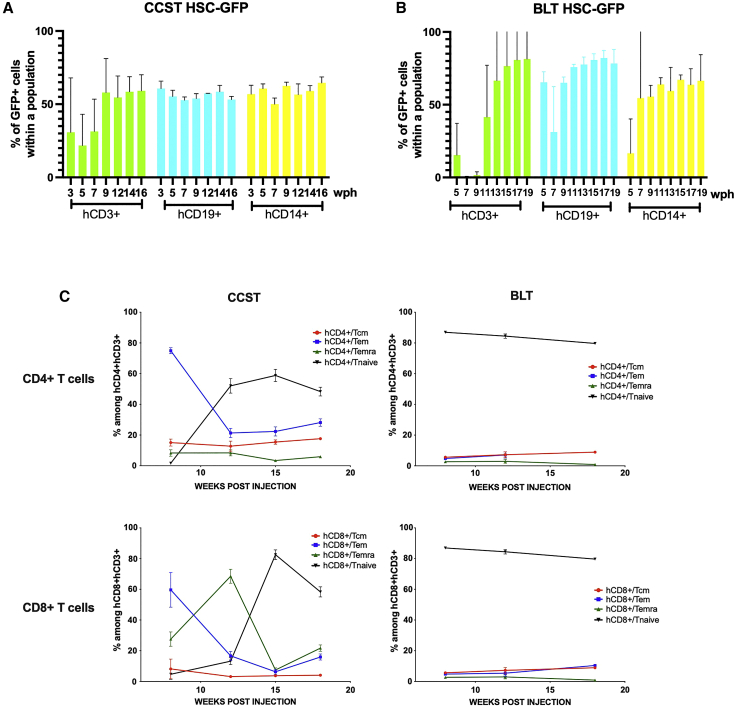
Figure 3.
Circulating human immune cells in CCST and BLT mice originate from engrafted CD34+ hematopoetic stem cells
Human HSCs were transduced with a GFP-expressing lentivirus. Transduction efficiency was 39% at the time of mouse engraftment. (A and B) Immune reconstitution data from (A) CCST (n = 3) and (B) BLT (n = 2) mice up to 19 weeks post humanization (wph). T cell (hCD3+), B cell (hCD19+), and monocyte (CD14+) compartments exhibited similar proportions of GFP-expressing cells. The y axis is indicative of the percentage of GFP+ cells within the population indicated in the x axis (either hCD3+, hCD19+, or hCD14+).
(C) Flow-cytometry analysis of the different subpopulation of T cells, namely T central memory (CD3+CCR7+CD45RA−), T effector memory (CD3+CCR7−CD45RA−), T effector memory re-expressing CD45R (EMRA, CD3+CCR7−CD45RA+), and naive T cells (CD3+CCR7+CD45RA+) populations in both CD4+ (top graphs) and CD8+ T cells (bottom graphs) of the CCST and BLT models (left and right columns, respectively).