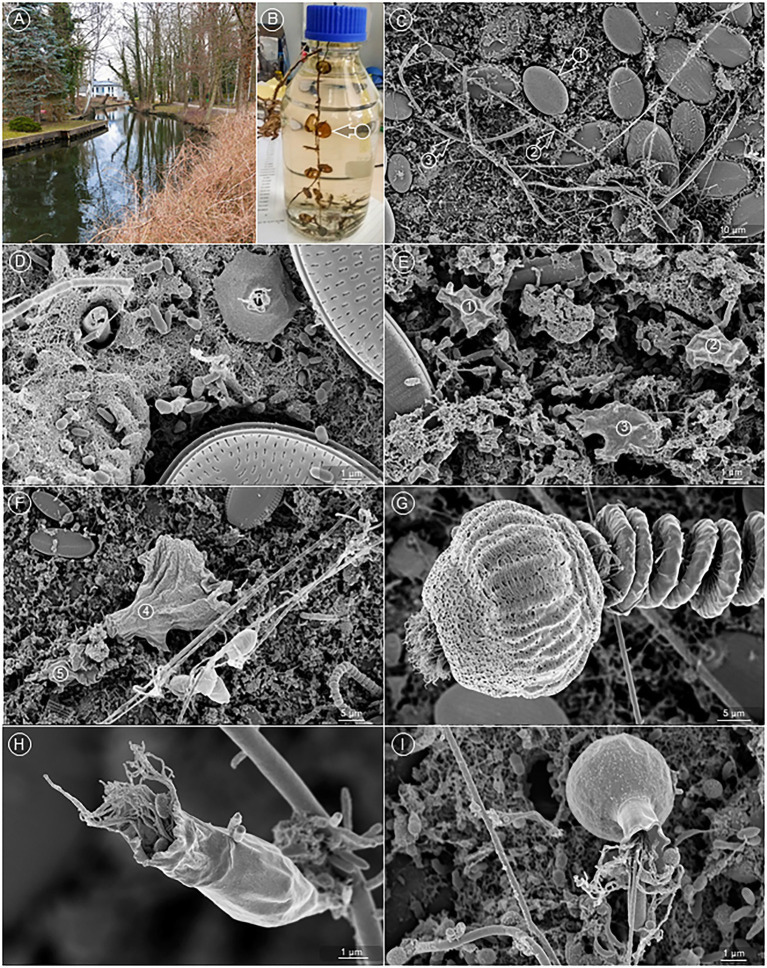
Figure 3.
An ex vivo biofilm from natural water. (A) Sampling location at the Bretter ditch in Brandenburg, Germany. (B) Sampled Thermanox™ coverslips (arrow) colonized with aquatic biofilm, transferred into a glass flask for the transport to the laboratory. (C) Overview of the biofilm. Readily visible are diatoms (arrow 1), bacteria, wrapped in a long, filamentous sheath (arrow 2), and hyphae of fungi (arrow 3). (D) The bottom layer of the biofilm is constituted by numerous bacteria, which are mostly embedded in a fibrous matrix. (E,F) Various amoebae were found on top of the bacterial bottom layer (circles 1–5). (G) Vorticella spp. were frequent constituents of the aquatic biofilm, (H,I) as were a great variety of other bacteria eating Ciliates.