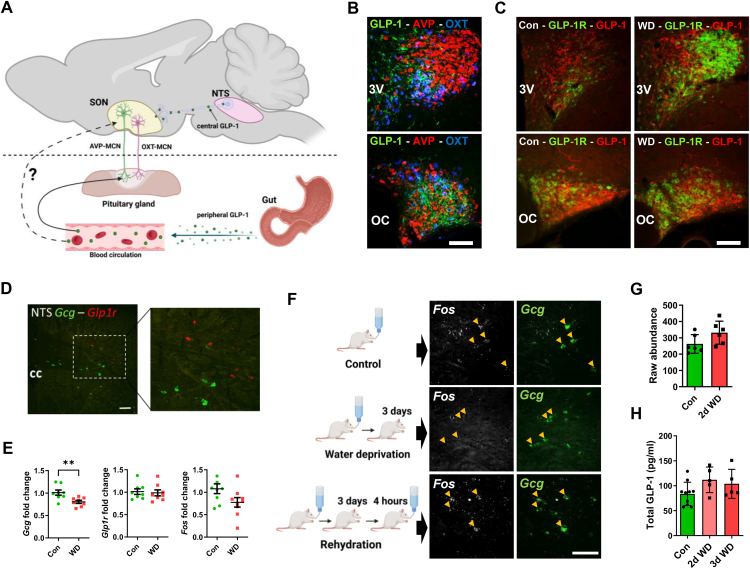
Figure 4.
GLP-1 inputs to the HNS. A, schematic showing the central (NTS) and peripheral (gut) sources of endogenous GLP-1 capable of signalling the MCN GLP-1R populations. B, immunostaining of active GLP-1 containing afferent fibers in the proximity of AVP and OXT neurones in the PVN and SON. C, immunostaining of active GLP-1 containing afferent fibres in the proximity of GLP-1R positive neurones in the PVN and SON of control and WD animals. D, in situ hybridisation of Gcg (green) and Glp1r (red) expressing cells in the rat NTS. E, qRT-PCR analysis of Gcg, Glp1r, and Fos mRNA expression in control and 3-day WD NTS samples. F, in situ hybridisation of Fos (white) and Gcg (green) expressing cells in the rat NTS in control, WD, and WD + 4 h rehydration. Arrow heads indicate Gcg positive neruones. G, total protein raw abundance of GCG in the SON according to LC-MS/MS between control and 2-day WD rats. H, plasma levels of total GLP-1 in samples from 2-day and 3-day WD rats. Values are means + SEM of n = 5–8 animals per group. OC, optic chiasm; 3 V, third ventricle; cc, central canal. ∗∗p ≤ 0.01. Scale bars = 100 μm.