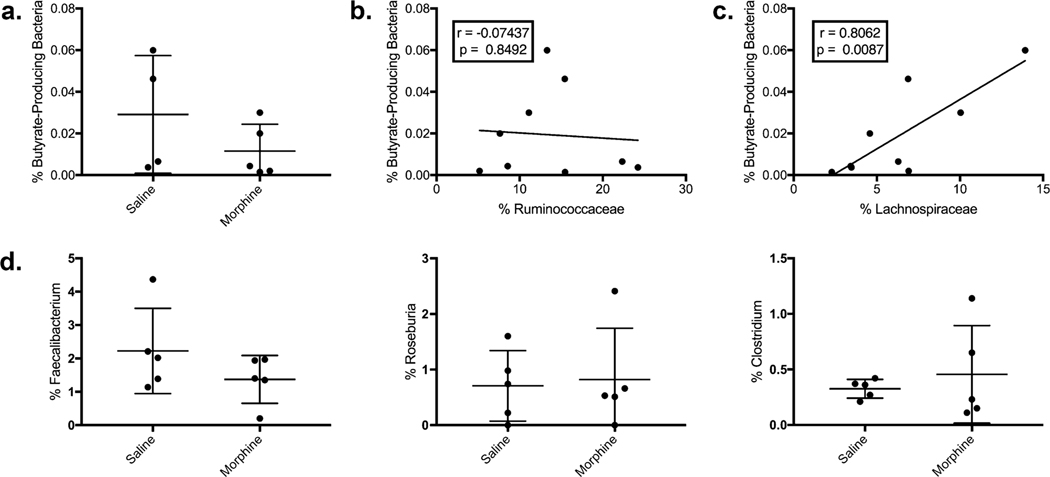
Fig. 5.
Loss of Ruminococcaceae was not associated with loss of total butyrate-producing bacteria (BPB): a To test whether the total relative abundance of BPB was statistically different between saline and morphine treatments, the relative abundance of Butyrl CoA-CoA Transferase genes was quantified and compared to the total 16S rRNA genes in isolated fecal DNA. b The relative abundance of BPB was not correlated with Ruminococcaceae in linear regression analysis but c was associated with Lachnospiraceae (r =0.8062, p = 0.0037), which was not statistically different in between groups in our analysis. d Morphine administration was not associated with significant changes in the largest BPB genera