Fig. 4.
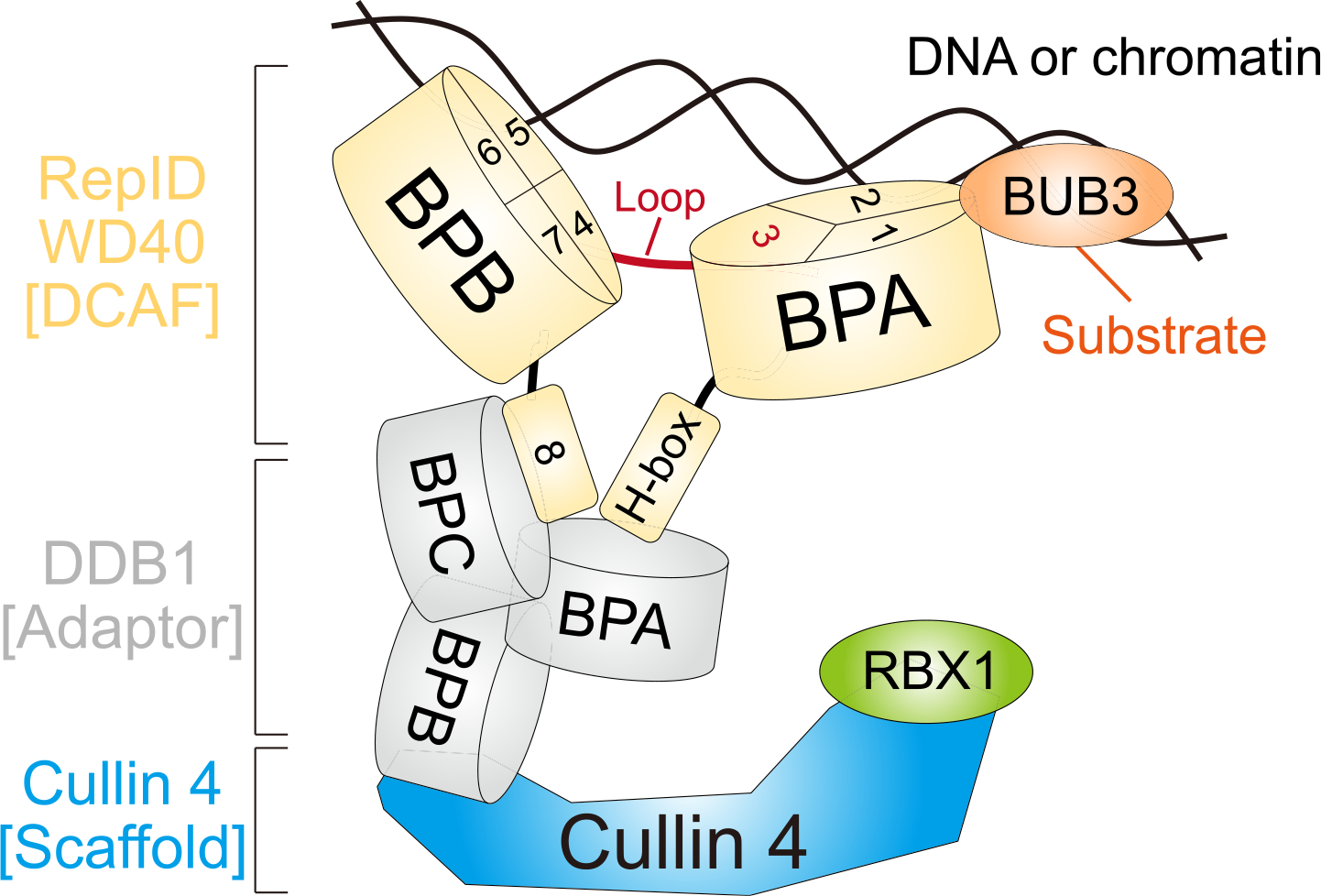
Schematic model. RepID WD40 domain consists of two β-propeller folds (RepID-BPA and BPB) and the loop structure positioned at exon 3 connects them. H-box locating N-terminal and exon 8 (blade 9) at the C-terminal region does not affect DNA/chromatin binding of the RepID but provides the platform for binding to BPA and BPC of DDB1 connected with CUL4 using BPB region. Two molecular clips of RepID (BPA and BPB) possibly recognize and interact with DNA/chromatin via exon 1–2 in BPA (blade 2–3) and exon 4–7 in BPB (blade 5–8). Therefore, the deleted form of BPA or BPB in RepID loses its DNA/chromatin binding ability, leading to compromised CRL4 recruitment. Exon 3 consists of blade 4, but also contains high amounts of loop structure which does not affect DNA/chromatin and CRL4 binding of RepID. BUB3 is located on chromatin in a RepID-independent manner and binds to exon 1 and 2 region in RepID-BPA.
