Figure 1.
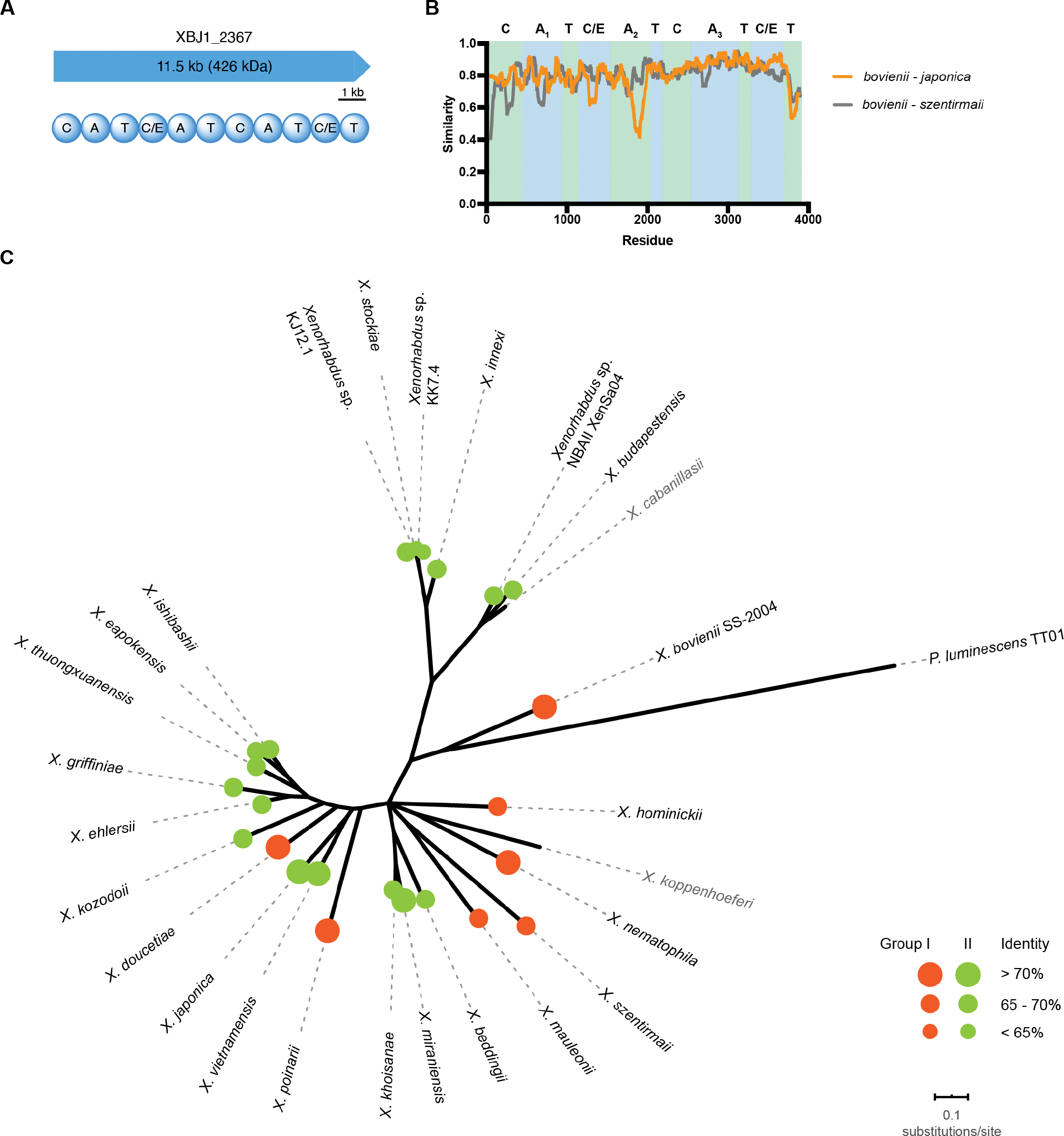
Domain architecture and distribution of XBJ1_2367 homologs in the genus Xenorhabdus. A, Domain architecture of NRPS XBJ1_2367. B, Sliding window analysis of amino acid sequences within group I (bovienii - szentirmaii) and between group I and II (bovienii - japonica). C, Unrooted phylogenetic tree of Xenorhabdus species and the distribution of XBJ1_2367 homologs. The maximum likelihood tree was based on the concatenated protein sequence alignments of five conserved housekeeping genes. Branches less than 50% of bootstrap frequencies were collapsed. Species without the gene homolog are shown in grey. Sizes of the circles represent protein sequence similarity to XBJ1_2367 (Orange circles: group I; Green circles: group II).
