FIGURE 3.
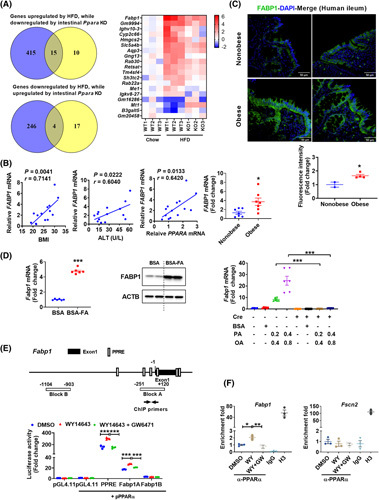
FABP1 is a target of intestinal PPARα. (A) Venn diagram and heat map. (B) correlation analysis of intestinal FABP1 mRNA expression with BMI, ALT, and PPARA mRNA levels (n = 14); mRNA levels of intestinal FABP1 in nonobese or obese humans (n = 7). (C) Representative immunofluorescence staining of FABP1 in human ileum (upper) and statistics (bottom); scale bar 50 µm. (D) Fabp1 mRNA (left) (n = 6) and FABP1 protein (middle) in fatty acid (0.4 mM palmitic acid plus 0.8 mM oleic acid)–treated PPARA‐humanized intestinal organoids, and Fabp1 mRNA (right) (n = 6) in primary Ppara fl/fl and Ppara ∆IE organoids treated with fatty acids for 24 h. (E) Schematic diagram of the mouse Fabp1 promoter illustrating the PPREs (upper) and luciferase reporter assay (bottom) (n = 3). (F) ChIP assay (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. BSA‐FA, BSA‐conjugated fatty acids
