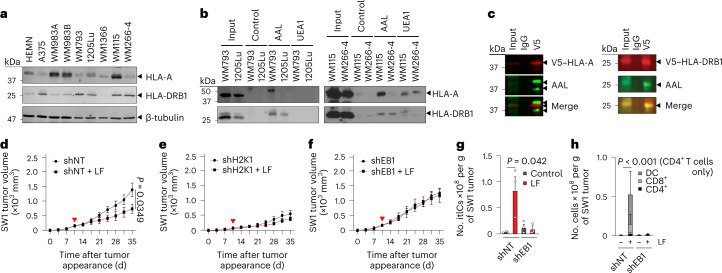
Fig. 3. HLA-DRB1 is expressed, fucosylated and required for l-fuc-triggered melanoma suppression and increased itIC abundance.
a, IB analysis of HLA-A and HLA-DRB1 levels in primary human melanocytes (HEMN) or the indicated human melanoma cell lines. b, LPD and IB analysis of patient-matched primary and metastatic cell line pairs WM793 and 1205Lu (left) and WM115 and WM266-4 (right) for HLA-A and HLA-DRB1. c, V5-immunoprecipitation and IB analyses of WM793 cells expressing (left) V5-tagged HLA-A or (right) V5-tagged HLA-DRB1. Volumetric growth curves for non-targeting control short hairpin RNA (shRNA) (shNT)- (d), H2K1-targeting shRNA (shH2K1)- (e) or H2EB1-targeting shRNA (shEB1)- (f) expressing SW1 tumors in C3H/HeN mice (n = 8 mice for each shNT group, n = 6 for each shH2K1 group and n = 6 and 7 for shEB1 and shEB1 with l-fuc groups, respectively). Flow cytometric comparison of total itIC counts (g) or the indicated subpopulations (h) from shNT- or shEB1-expressing tumors in d,f. n = 3 mice per group. For d–f, the red triangle indicates initiated l-fuc supplementation; growth curves and column charts show mean ± s.e.m. from each mouse group. In a–c, representative images are shown for n = 3 independent biological replicate experiments.