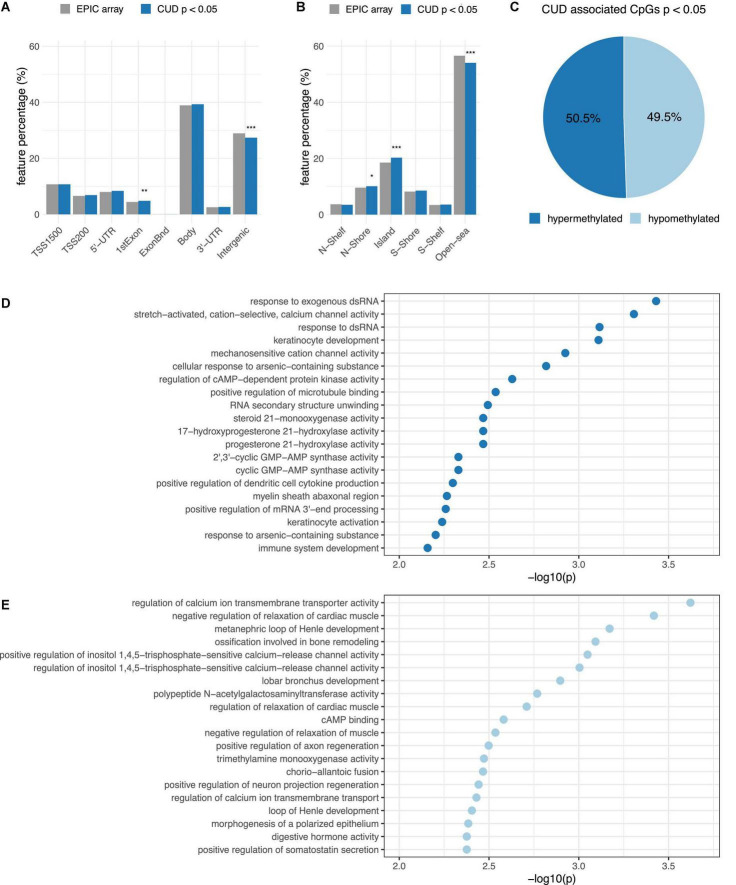
FIGURE 2.
Results from the epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) of CUD were prioritized based on association p-values resulting in a subset of N = 29,176 CpG sites with passoc < 0.05 that was further analyzed by annotation to panel (A) gene regulatory features and (B) the CpG island (CGI) background. The proportion of CUD-associated CpG sites (blue) within different groups was compared to the EPIC array background (gray). Differences remaining statistically significant after Bonferroni multiple testing correction are highlighted using asterisks (* = padj < 0.05, ** = padj < 0.01, *** = padj < 0.001). (C) Hypermethylation (light-blue) and hypermethylation (dark blue) among the N = 29,176 CUD-associated CpG sites. The top 20 CUD-associated GO terms resulting from missMethyl (42) are shown for (D) hypermethylated and (E) hypomethylated CpG sites associated with CUD (p < 0.001).