FIGURE 1.
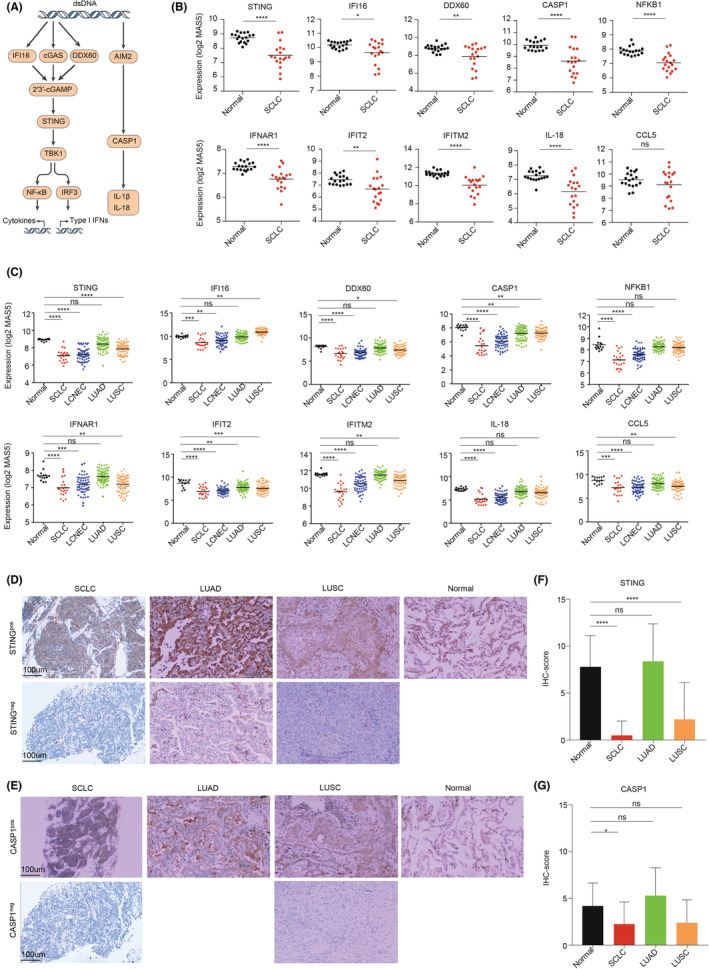
Expression of STING signaling‐related genes is reduced in SCLC. (A) Schematic of dsDNA sensing pathways that activate STING pathway and induce type I IFNs. (B) Relative mRNA expression of STING signaling‐related genes in SCLC and paired normal lung tissues. (C) Relative mRNA expression of STING signaling‐related genes among different histological subtypes in the lung. (D, E) Representative IHC staining images of STING (D) and CASP1 (E) in SCLC, LUAD, LUSC, and normal lung tissues. (F, G) IHC score of STING (F) and CASP1 (G) expression in SCLC, LUAD, LUSC, and normal lung tissues. LCNEC, large cell neuroendocrine cancer; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; ns, not significant. p values were calculated by unpaired t‐test (B) and one‐way ANOVA (C, F, and G). p values of statistical significance are represented as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.
