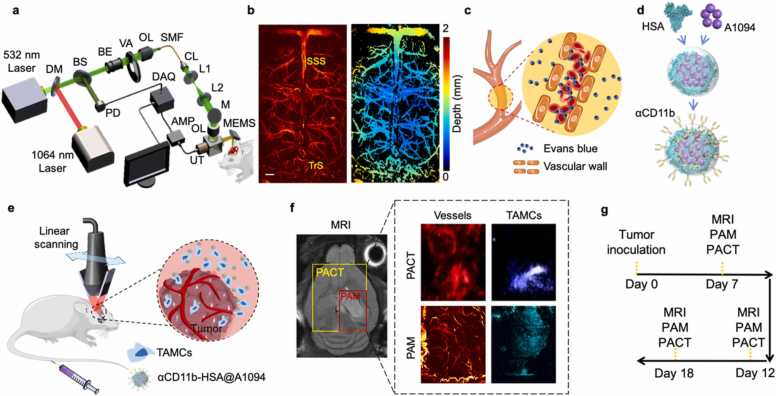
Fig. 1.
The multi-wavelength photoacoustic molecular imaging approach for in vivo assessment of GBM neovascularization and TAMCs. (a) Schematic of MEMS-based PAM system for transcranial imaging. DM, dichroic mirror; BS, beam splitter; PD, Photodiode; BE, beam expander; VA, variable attenuator; OL, objective lens; SMF, single-mode fiber; CL, collimating lens; M, mirror; UT, ultrasonic transducer; MEMS, microelectromechanical systems; AMP, amplifier; DAQ, data acquisition card. (b) Representative PAM image of normal mouse brain cortex and its depth encoding image (scale bar = 500 µm). (c) Imaging GBM neovascularization and vascular permeability changes by PAM. (d) A brief synthesis diagram of TAMCs targeted nanoprobe, αCD11b-HSA@A1094. (e) Schematic diagram of TAMCs tracing by PACT in an orthotopic GBM model. (f) The distribution of cerebral cortex vessels and TAMCs by dual-wavelength PACT (970 and 1200 nm) and PAM (532 and 1064 nm) approaches (yellow and red boxes in the MRI image indicated the imaging region of PACT and PAM, respectively). SSS, superior sagittal sinus; TrS, transverse sinus; HSA, human serum albumin; TAMCs, tumor-associated myeloid cells. (g) Diagram of tumor inoculation and imaging timeline.