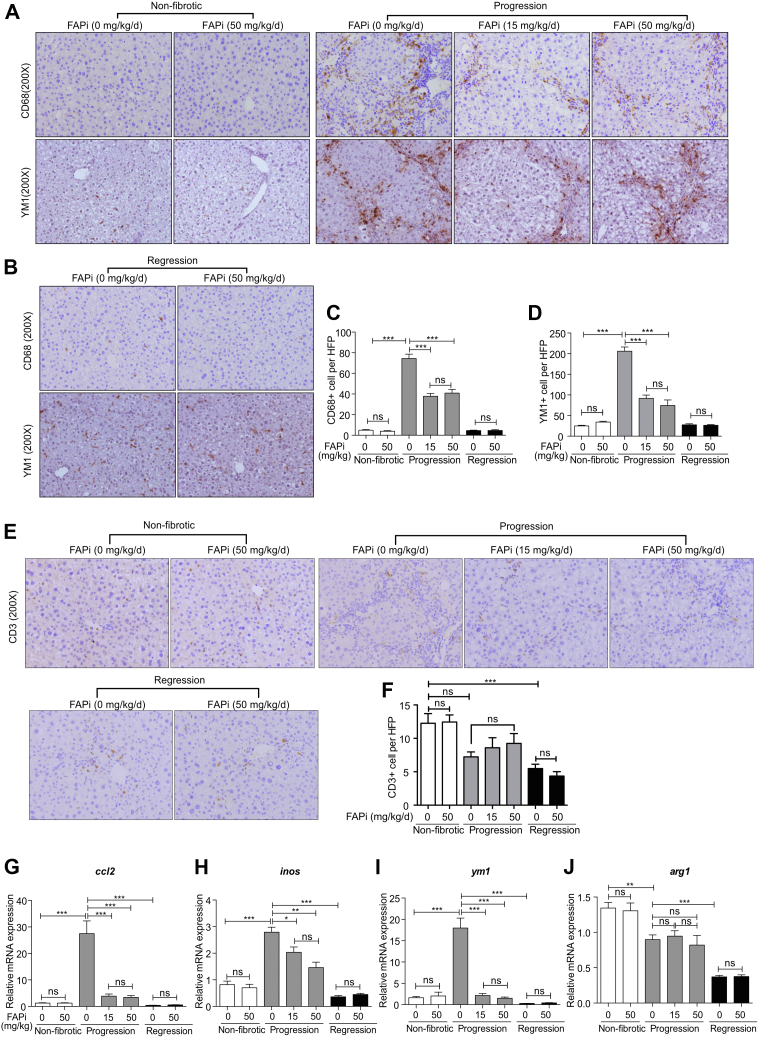
Figure 3.
Effect of FAP inhibition on hepatic inflammation in CCl4-induced fibrosis. (A–D), Livers from non-fibrotic mice and mice with fibrosis progression or regression (n = 5–10/group) treated with FAPi and controls were analyzed for macrophage markers CD68 and YM1 using immunohistochemistry in 10 random high-power fields per liver. (E–F), Representative images and quantification of CD3+ T cells in 10 random fields (×200) from the central right lobe of each liver. (G–J), Hepatic transcript levels of inflammation related genes. Data in (C–D, F, G–J) are means ± standard error of the means (SEMs). Statistical analysis was performed as for Figure 1.