FIG 5.
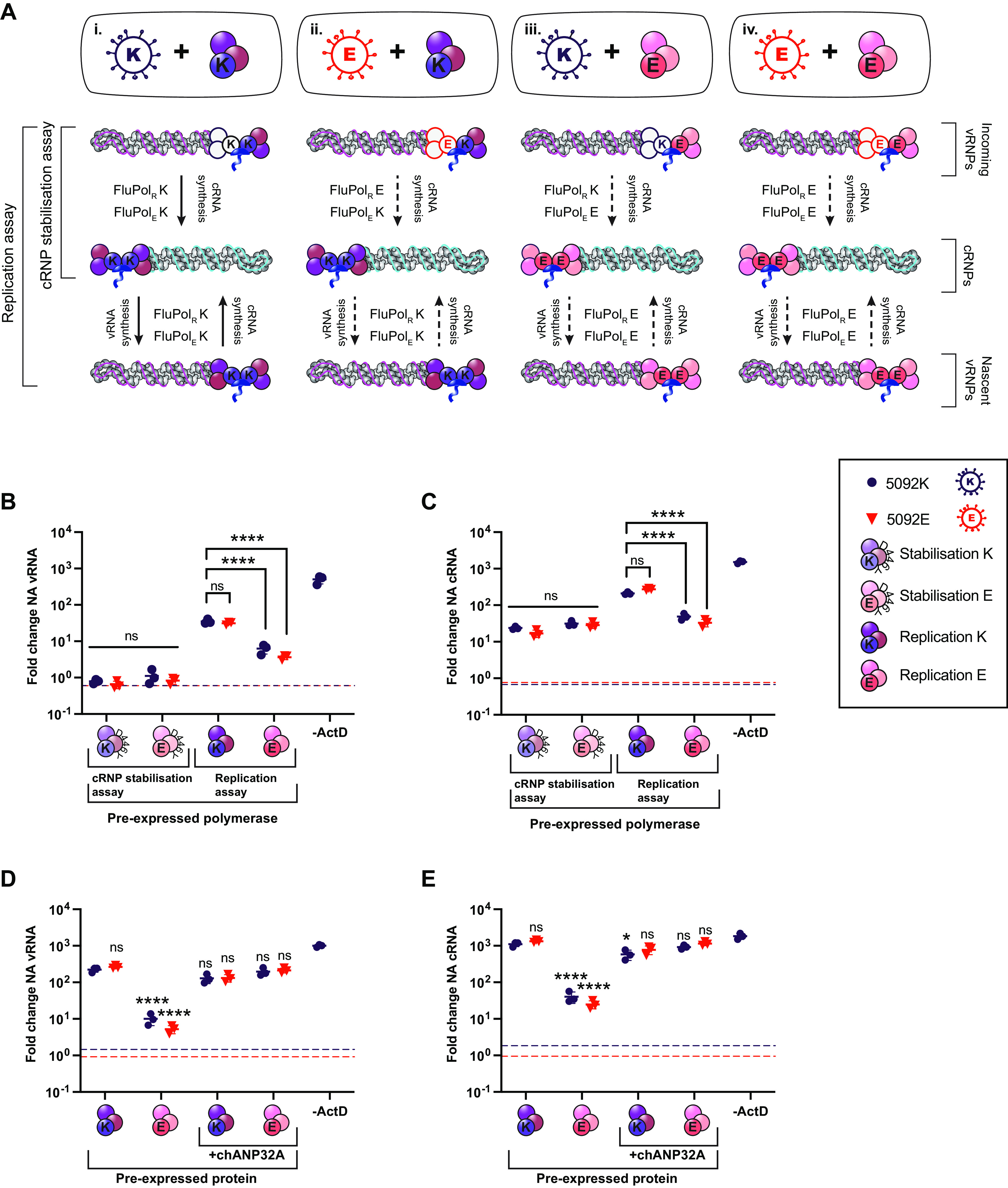
Avian polymerase is not restricted in cRNA synthesis in mammalian cells. (A) Schematic outlining assay setup and expected polymerase combinations during replication. As indicated on the left, in the cRNP stabilization assay, only the first layer of activity (primary cRNA synthesis) will occur. Both layers of activity can occur in replication assays. Unknown polymerase activity is indicated by a dashed black arrow. (B and C) Simultaneous cRNP stabilization and replication assays with ActD, 6 hpi. Segment 6 vRNA (B) and cRNA (C) accumulation following infection with either 5092E or 5092K as indicated (MOI = 0.1) is shown. The dotted line indicates levels of vRNA/cRNA present in a control lacking PB2 in the transfection mix. The fold change was calculated versus input (0 hpi). n = 3 biological replicates, plotted as means ± the SD. Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test, following log transformation. (D and E) Replication assays with ActD and chANP32A, 6 hpi. Segment 6 vRNA (D) and cRNA (E) accumulation following infection with either 5092E or 5092K as indicated (MOI = 0.1) is shown. The dotted line indicates the levels of vRNA/cRNA present in a control lacking PB2 in the transfection mix. The fold change was calculated over input (0 hpi). n = 3 biological replicates, plotted as means ± the SD. Significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test, following log transformation. Pre-expressed polymerase mixes: stabilization K = PB2 627K, PB1 D446Y, PA, and NP; stabilization E = PB2 627E, PB1 D446Y, PA, and NP; replication K = PB2 627K, PB1, PA, and NP; replication E = PB2 627E, PB1, PA, and NP. ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001.
