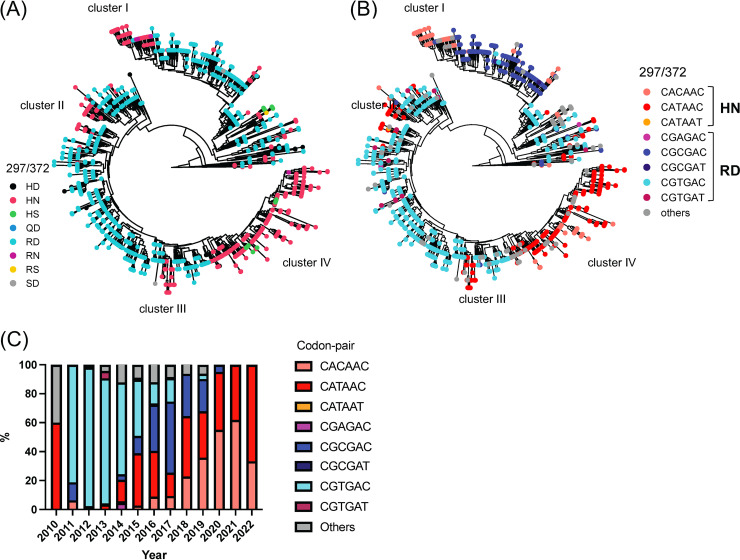
FIG 6.
Amino acid mutational pattern from antigenic site A from GII.4 Sydney_2012 variant is associated to differential genetic codon usage. (A) Amino acid distribution in the phylogenetic trees shows evolutionary convergence in residues 297 and 372 from major capsid protein (VP1) of GII.4 Sydney_2012 noroviruses. (B) Phylogenetic tree color-coded based on the codon presented for the codon pair encoding residues 297 and 372. (C) Temporal genetic diversification of the codon pair encoding amino acids 297 and 372. Colors of the bars correspond to the most frequent sequence patterns presented at those 2 codon positions. The analyses were done using 1,449 complete (or nearly complete) sequences of Sydney_2012 noroviruses. The phylogenetic trees were calculated as indicated in Fig. 1 and the Materials and Methods section. Clusters were arbitrarily assigned, in order to facilitate description, to monophyletic branching of strains with similar codon pair usage.