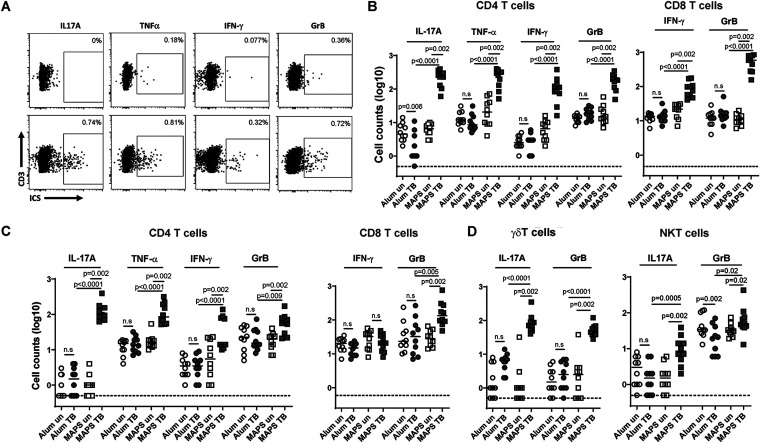
FIG 4.
Immunization with MAPS2 leads to differentiation and expansion of a diversity of functional T cells in spleens and lungs. Mice were immunized three times with Alum or MAPS2 as described in the legend to Fig. 3. Six months later, spleens and lungs were collected, and the cells were left unstimulated (U) or stimulated with a mixture of Mtb proteins (S). The production of cytokines or cytotoxic molecules in different T cell populations was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Representative dot plots of lung CD4+ T cells of Alum- (Alum TB) or MAPS2-immunized mice (MAPS TB) that produce IL-17A, TNF-α, IFN-γ, or granzyme B (GrB) post-stimulation. (B) Absolute counts of IL-17A-, TNF-α-, IFN-γ-, or GrB-producing CD4+ (CD3+ TCRβ+ NK1.1− CD4+ CD8−) or CD8+ (CD3+ TCRβ+ NK1.1− CD4− CD8+) T cells in 1/80 of total splenocytes isolated from Alum- (circles) or MAPS2-immunized (squares) mice without (un) and with Mtb protein stimulation (TB). (C) Absolute counts of IL-17A-, TNF-α-, IFN-γ-, or GrB-producing CD4+ or CD8+ T cells in the lung (1/5) of Alum- or MAPS2-immunized mice before and post-stimulation. (D) Absolute counts of IL-17A- or GrB-producing γδT cells (CD3+ TCRβ− NK1.1−) and NKT cells (CD3+ TCRβ+ NK1.1+) in 1/5 of total lung cells (including both lobes) isolated from Alum- (circles) or MAPS2-immunized (squares) mice without (un) and with Mtb protein stimulation (TB). n = 5 mice per group per analysis. The data represents a summary of two individual analyses. Lines indicate medians. Dotted lines represent the lower detection limit. n.s., not significant.