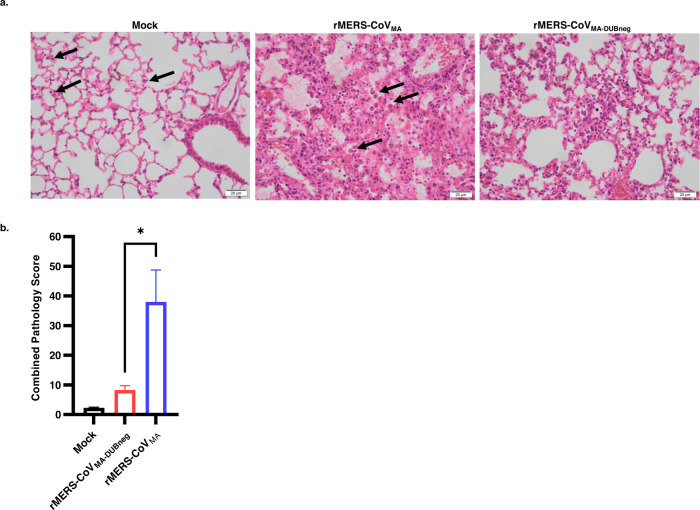
Fig. 3. Lung pathology of mock-, rMERS-CoVMA-, and DUB-negative rMERS-CoVMA-infected hDPP4 KI mice on day 4 post infection.
Groups of 4 animals (n = 4) were intranasally inoculated with 50 µL DMEM containing either 104 PFU virus or no virus (mock), sacrificed at day 4 post infection and subsequently examined microscopically. a Photomicrographs of representative lung lesions are shown from mock- (left panel), rMERS-CoVMA- (middle panel), or rMERS-CoVMA-DUBneg- (right panel) infected animals (H&E stain, ×400 magnification). Compared with the mock-infected animals, which only exhibited occasional alveolar macrophages (arrows), the rMERS-CoVMA-infected animals had a diffuse, lymphohistiocytic, interstitial pneumonia with moderate amounts of predominantly macrophages (arrows) and fewer lymphocytes/plasma cells and viable neutrophils. The rMERS-CoVMA-DUBneg-infected animals also had an interstitial pneumonia of similar character, but less extensive in severity and distribution. The asterisk indicates an inflammatory focus with increased numbers of alveolar and interstitial macrophages and viable neutrophils. b Bar chart with semi-quantitative combined lung pathology scores. Bar heights indicate group means (n = 4) and error bars the standard error of the mean. The difference between the rMERS-CoVMA and rMERS-CoVMA-DUBneg groups reached statistical significance (Student’s t test, unpaired, *P<0.0336). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.