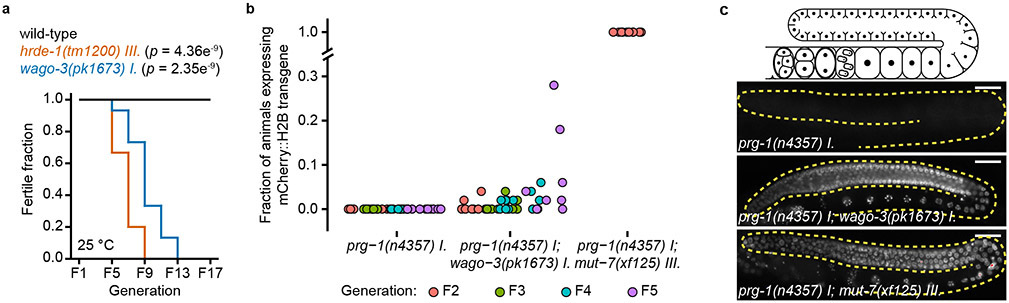
Extended Data Fig. 1. WAGO-3 is required for germline immortality and transgenerational maintenance of RNAe.
a, Mortal germline assay representing loss of fertility of strains with indicated genotype at 25°C. Statistical significance was tested with a log-rank-test (n = 15 populations per strain assayed in a single experiment). b, Diagram displaying mCherry::H2B(RNAe) reactivation in prg-1(n4357), prg-1(n4357);mut-7(xf125) and prg-1(n4357);wago-3(pk1673) mutant generations. F2-F5: second-fifth homozygous generation. For each generation, reactivation in 10 populations of 50 animals each was scored. Each plotted point represents the fraction of 50 animals that express the mCherry::H2B transgene. Since no prg-1(n4357) single mutant animal was found to reactivate mCherry::H2B expression, the value of this group is deterministically zero due to lack of variability/statistical noise. Thus, any positive number of animals that expresses the mCherry::H2B transgene in either the prg-1(n4357);mut-7(xf125) or prg-1(n4357);wago-3(pk1673) group causes a significant difference from the prg-1(n4357) group. c, Micrographs of three example animals with the mCherry::H2B transgene in either RNAe (prg-1(n4357)) or activated (prg-1(n4357);wago-3(pk1673) and prg-1(n4357);mut-7(xf125)) status. Top panel shows schematic representation of an adult hermaphroditic gonad. Activity status of the transgene was homogeneous in F2 homozygous prg-1(n4357) and prg-1(n4357);mut-7(xf125) mutants. Images represent two biologically independent experiments. Scale bars: 30 μm. Source data are provided.