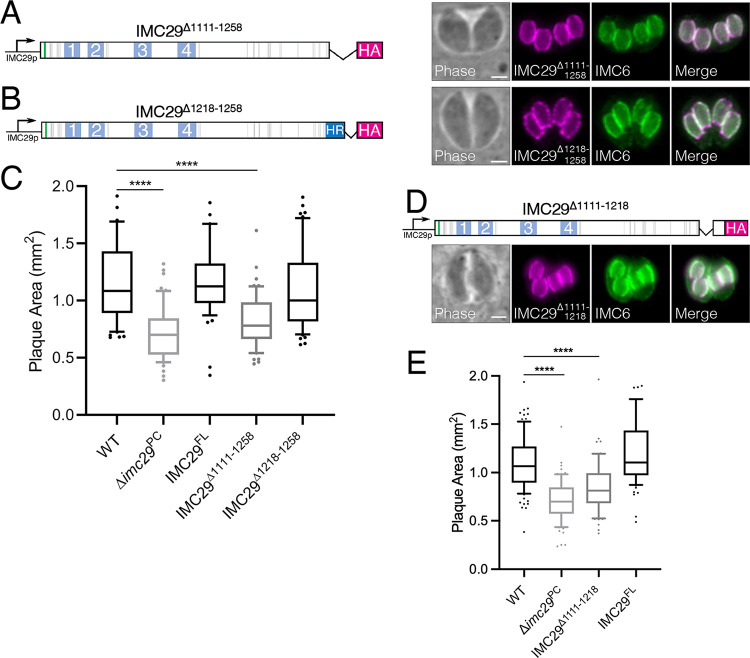
FIG 6.
IMC29 function is dependent on a short C-terminal region. (A) Diagram and IFA of IMC29Δ1111-1258, which removes the C-terminal predicted helical region as well as the remaining C-terminal end, shows that daughter IMC localization remains intact. (B) Diagram and IFA of IMC29Δ1218-1258, which removes only the extreme C-terminal end, shows proper daughter IMC localization. (C) Plaque assays show that while IMC29Δ1218-1258 rescues the plaque defect, IMC29Δ1111-1258 does not. Significance was determined using multiple two-tailed t tests. ****, P < 0.0001. (D) Diagram and IFA of IMC29Δ1111-1218, which removes only the C-terminal predicted helical region, shows that daughter IMC localization is unaffected. (E) Plaque assay indicates that IMC29Δ1111-1218 cannot rescue IMC29 function. Significance was determined using multiple two-tailed t tests. ****, P < 0.0001. For all IFAs: magenta, mouse anti-HA; green, rabbit anti-IMC6. All scale bars are 2 μm.