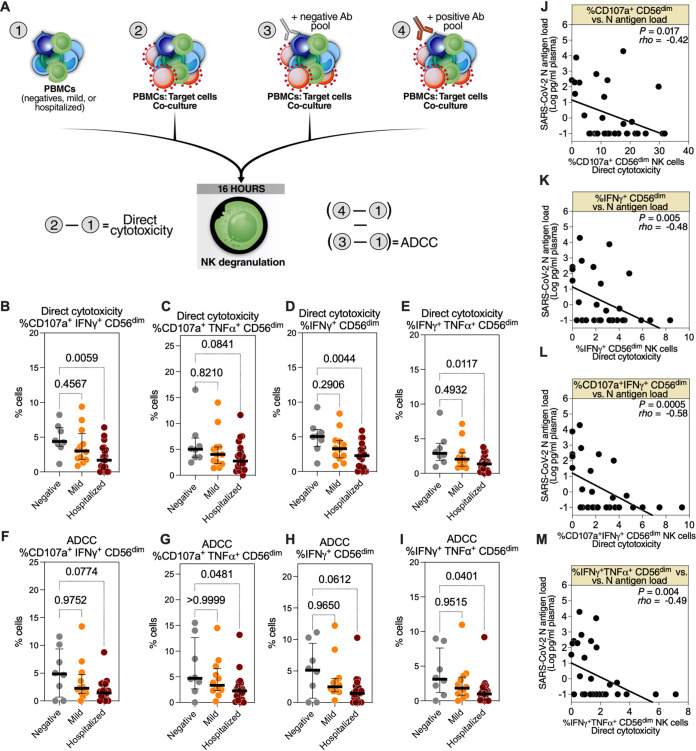
FIG 1.
Hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is associated with reduced CD56dim natural killer (NK) cell degranulation against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike-expressing target cells. (A) Schematic overview of the experiments to evaluate the direct cytotoxicity- and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC)-mediated degranulation of CD56dim NK cells during different severities of COVID-19. To examine direct cytotoxicity-mediated degranulation, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from each donor, from three COVID-19 status groups (n = 8 SARS-CoV-2 negative, n = 12 mild COVID-19, and n = 21 hospitalized COVID-19), were cocultured (2) or not (1) with SARS-CoV-2 Spike-expressing 293T target cells. To examine ADCC-mediated degranulation, identical cocultures were performed in the presence of the negative (3) or positive (4) antibody pool. Direct cytotoxicity was assessed by subtracting (1) from (2). 10:1 effector:target [E:T] ratio. ADCC was assessed by subtracting the results of subtracting (1) from (3) from the results of subtracting (1) from (4). (B to E) Direct cytotoxicity-mediated degranulation and cytokine production of the CD56dim NK population was assessed as the percentage of (B) CD107a+ interferon γ (IFN-γ)+, (C) CD107a+ tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)+, (D) IFN-γ+, and (E) IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ cells. Medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) are displayed. Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn’s multiple comparisons correction were used for statistical analyses. (F to I) ADCC-mediated degranulation and cytokine production of the CD56dim NK population was assessed as the percentage of (F) CD107a+ IFN-γ+, (G) CD107a+ TNF-α+, (H) IFN-γ+, or (I) IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ cells. Median and IQR are shown. Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn’s multiple-comparisons correction were used for statistical analyses. (J to M) Spearman’s rank-order correlations between plasma N-antigen load and the percentage of CD56dim NK cells expressing (J) CD107a+, (K) IFN-γ+, (L) CD107a+ IFN-γ+, and (M) IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ during direct cytotoxicity assays; only samples from COVID-19-positive donors were used (n = 33).