Figure 3. Hazard ratios (95% CI) of atrial fibrillation by quartiles of cumulative average uric acid in the total sample and stratified by incident hypertension, diabetes, heart failure, or coronary heart disease during follow‐up.
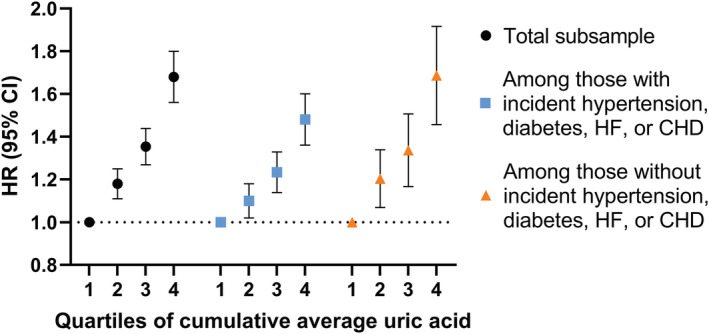
All hazard ratios were adjusted for age, sex, total cholesterol, glucose, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and triglycerides at the time of first uric acid measurement. CHD indicates coronary heart disease; HF, heart failure; and HR, hazard ratio.
