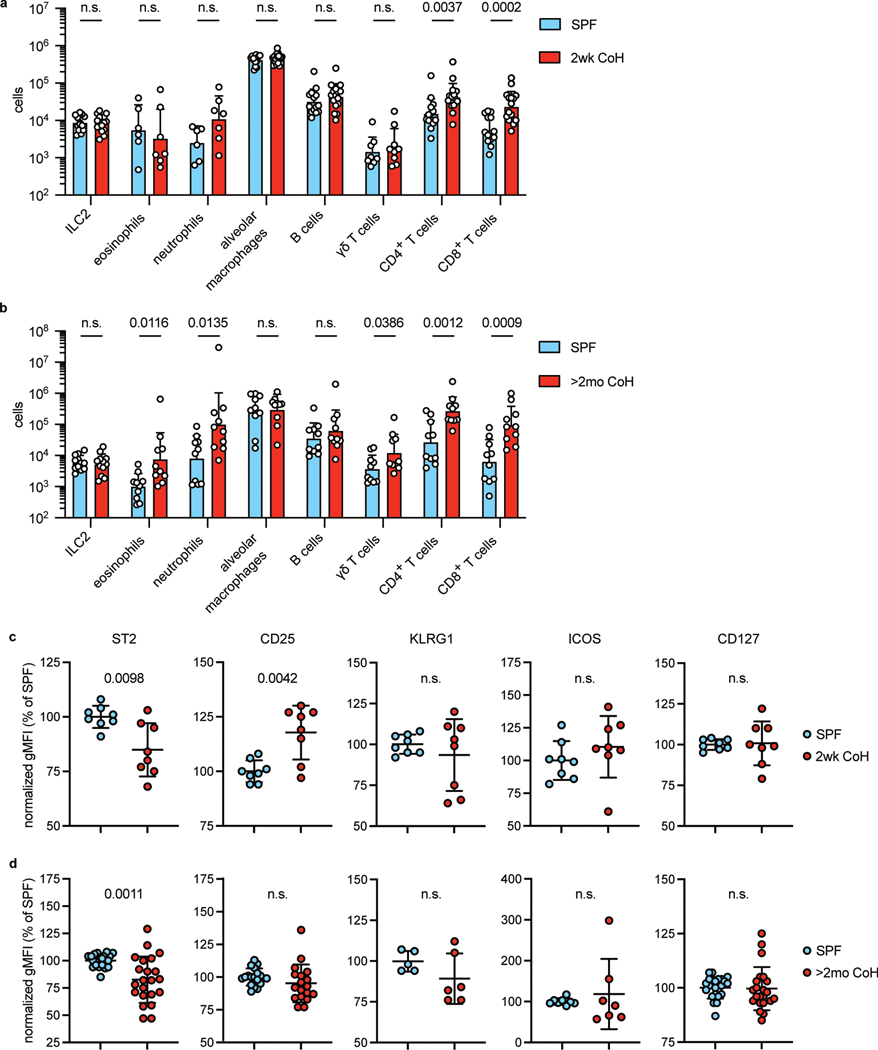
Fig. 1. Mouse lung immune cell populations are altered by cohousing.
a, Lung immune cell populations of age matched SPF and two-week cohoused (2wk CoH) B6 mice were identified and quantified by flow cytometry. All enumerated cells were i.v. CD45− except alveolar macrophages. Pooled from 7 experiments (n = 6–16/group). b, Lung immune cells quantified from age matched SPF and B6 mice cohoused for at least two months (>2mo CoH). Pooled from 3 experiments (n = 8–12/group). a, b Bar graphs show mean +SD of log transformed values. Each symbol represents a mouse. P values were determined with a Student’s t-test (two-tailed). Eosinophils in SPF vs. >2mo CoH had unequal variance and t-test was conducted with Welch’s correction; n.s. p ≥ 0.05. c-d. Geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of surface proteins on lung ILC2 in age-matched SPF and CoH mice. gMFI normalized to SPF groups in each experiment. c, Two-week cohoused and age-matched SPF mice. Pooled from 3 experiments (n = 8/group). Data are presented as mean values +SD. d, Two-month and age-matched SPF mice. Pooled from 5 experiments (CD25, n = 18/group), 6 experiments (ST2 and CD127, n = 22/group), and two experiments (ICOS, n = 7–8/group), KLRG1, n = 5–6.group). P values were determined with a Student’s t-test (two-tailed). In comparisons with unequal variance a t-test was conducted with Welch’s correction; n.s. p ≥ 0.05. Source Data contains exact P-values and group sizes.