Figure 1.
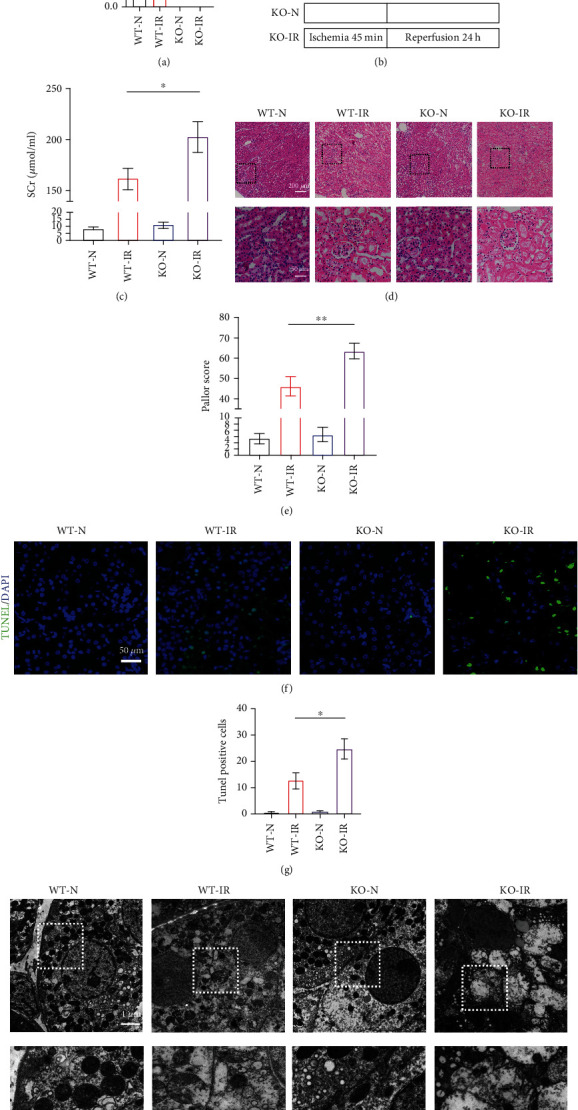
ALDH2 deficiency exacerbates renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. WT mice and ALDH2−/− mice were subjected to either sham operation or kidney ischemia for 45 minutes and reperfusion for 24 hours. (a) Kidney lysates from WT mice and ALDH2−/− mice were subjected to western blot analysis for ALDH2. n = 3/group. (b) An illustration of the injury model used in this study. (c) Serum creatinine (SCr) were measured after 24 h of reperfusion. n = 6/group. (d) H&E staining showed renal tubule epithelial cell injury and red blood cell deposition. Scale bar: 200 μm, 50 μm. (e) Paller score was performed using a semiquantitative damage assessment of renal tubular epithelial cells for each sample. n = 6/group. (f) Representative images of TUNEL staining (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 100 μm. (g) The percentage of TUNEL staining-positive cells in the total cells in the random field. n = 3/group. (h) Morphology of renal tubular epithelial cell was observed under TEM. n = 3/group. Scale bar: 20 μm, 10 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 by t-test.
