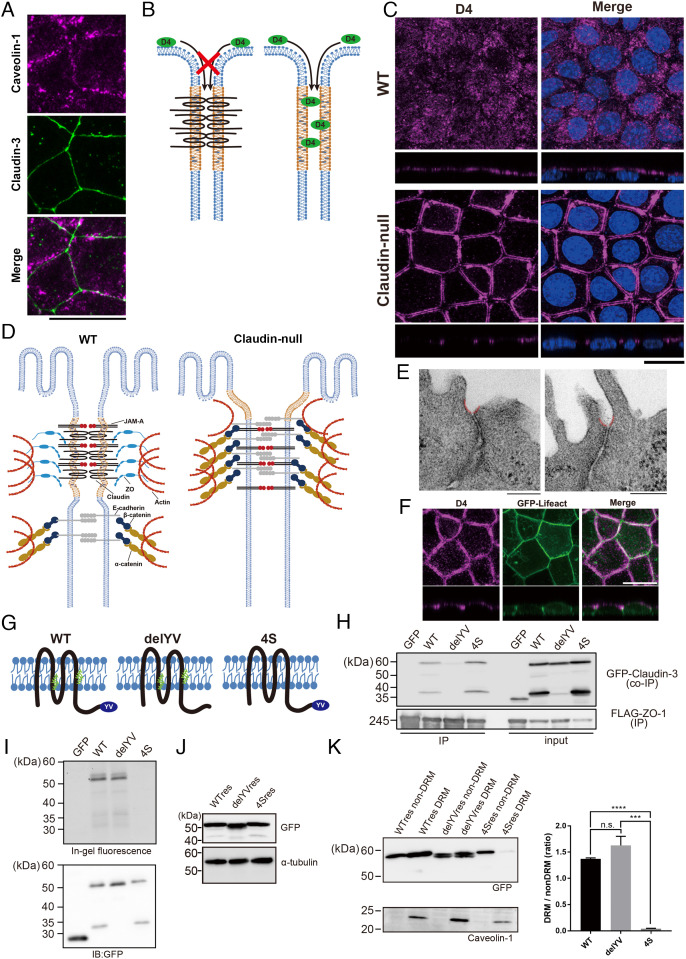
Fig. 3.
Accumulation of cholesterol at AJCs is maintained without TJs in claudin-null cells. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of EpH4 WT stained for caveolin-1 and claudin-3. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (B) Schematic of the cholesterol localization analysis using the cholesterol-binding protein, RFP-D4. RFP-D4 cannot access the lateral membrane in WT cells because its bulk and hydrophilicity prohibit its passage across the TJ barrier. Under conditions where the barrier is absent, such as in claudin-null cells, RFP-D4 is able to access the lateral membrane, enabling direct verification of either the presence or the absence of cholesterol enrichment around AJCs. (C) Distribution of cholesterol at the outer leaflet of plasma membrane visualized by D4 staining in EpH4 WT and claudin-null cells. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (D) In claudin-null cells, the intrinsic contractility of the actomyosin ring anchoring AJCs pulls apart the more apical membrane regions between adjoining cells since they are no longer tethered by TJs. The gap between parallel D4 staining in Fig. 2B reflects this disassociated state at the presumptive TJ region. (E) Representative transmission EM images of ultrathin sections of claudin-null cells. In claudin-null cells, the plasma membrane regions immediately apical to AJCs is caved inward (colored red). (Scale bars, 200 nm.) (F) Representative fluorescence images of GFP-Lifeact-expressing claudin-null cells stained with RFP-D4. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (G) Molecular schematic of claudin mutants. The delYV mutant lacks the C-terminal PDZ-binding motif (YV) that is essential for binding to ZO proteins. In the 4S mutant, all four cysteine residues that undergo palmitoylation (green) were changed to serine. (H) Binding of GFP-fused claudin mutants to ZO-1 was assessed by immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged ZO-1. (I) Palmitoylation was detected using fluorescent palmitic acid. As expected, fluorescent palmitic acid is not incorporated by the 4S mutant. (J) Establishment of claudin-null cells stably expressing GFP-fused WT res, the delYV mutant (delYV res), or the 4S mutant (4S res). Whole-cell lysates were blotted with anti-GFP antibody and anti-alpha tubulin antibody. (K) Immunoblot analysis of the DRM and non-DRM fractions of claudin-null cells stably expressing WT claudin-3 (WT res), the delYV mutant (delYV res), or the 4S mutant (4S res). The DRM fraction is enriched with the DRM marker protein caveolin-1. The ratio of protein levels between DRM and non-DRM fractions were quantified (n = 3, Student’s t test, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).