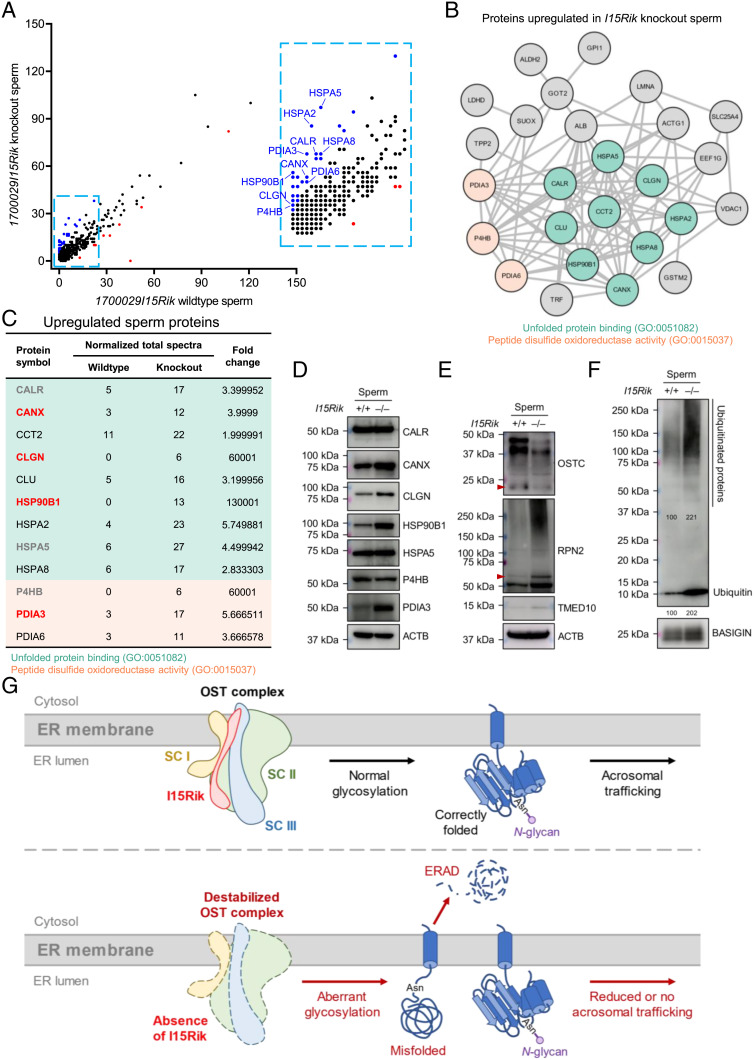
Fig. 5.
Ablation of 1700029I15Rik Results in Upregulated ER Chaperones and Ubiquitinated Proteins in the Sperm. (A) MS analysis of wild-type and 1700029I15Rik knockout sperm proteome. Blue and red dots indicate proteins upregulated and downregulated in the knockout spermatozoa, respectively. (B) STRING (20, 21) and GO (22) analyses of proteins upregulated in 1700029I15Rik knockout spermatozoa. The proteins related to unfolded protein binding (GO:0051082) or exhibited peptide disulfide oxidoreductase activity (GO:0015037) are highlighted in teal and light orange, respectively. (C) Upregulated ER chaperones in 1700029I15Rik knockout spermatozoa. The upregulation of CANX, CLGN, HSP90B1, and PDIA3 (highlighted in bold font and red color), but not CALR, HSPA5, and P4HB (in bold font and gray color), have been verified by Western blot analyses shown in Fig. 5D. (D) Western blot analyses of multiple ER chaperones in wild-type and knockout spermatozoa. ACTB was analyzed as a loading control. (E) Western blot analyses of OSTC, RPN2, TMED10 in wild-type and knockout spermatozoa. ACTB was analyzed as a loading control. (F) Western blot detection of ubiquitin and ubiquitinated proteins in wild-type and knockout spermatozoa. BASIGIN was analyzed in parallel as a loading control. The band intensities relative to BASIGIN were measured by ImageJ. The numbers represent the relative intensities of ubiquitinated proteins (Upper) or ubiquitin (Lower). (G) A diagram depicting 1700029I15Rik-mediated processing of acrosomal membrane proteins. OST complex is composed of subcomplex (SC) I, II, and III. Briefly, 1700029I15Rik interacts with and stabilizes OSTC and RPN2, which localize to SC II and SC III, respectively (28). In the absence of 1700029I15Rik, the destabilized OST complex causes aberrant glycosylation of acrosomal membrane proteins, resulting in increased protein misfolding. The misfolded proteins are eliminated by ubiquitin-dependent ERAD. Thus, the acrosomal trafficking of mature proteins is reduced or impaired.