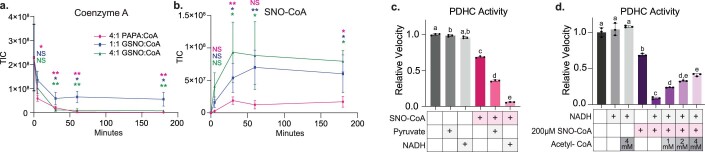
Extended Data Fig. 3. SNO-CoA delivers RNS modifications to the lipoic arm.
a-b. The decrease in CoA level (a) and the appearance of SNO-CoA (b) over time after CoA was mixed with NO donor PAPA NONOate or GSNO at indicated ratio. Statistical difference between each time point comparing to time 0 was determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests. NS specifies not significant (p>0.05), * signifies p≤0.05, ** signifies p≤0.01. Color of significance indicator corresponds to respective condition with the same color. Exact P-values for each comparison are available in Source Data. Symbol and error bars represent mean ± SD, n=3 distinct samples. TIC, total ion count. c. The activity of purified PDHC after 3h incubation (RT) with ± 200µM SNO-CoA ± 200µM pyruvate ± 200µM NADH, as indicated on figure. d. The activity of purified PDHC after 1h incubation (RT) with 200µM SNO-CoA, 200µM NADH and acetyl-CoA at various doses as indicated. After incubation period and immediately prior to activity measurement, varying amount of acetyl-CoA was added to samples to even out the final acetyl-CoA concentration across all reactions. c-d. Bars and error bars represent mean ± SD, n=3 distinct samples. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Those bars not sharing a letter are significantly different from each other (p<0.05). Exact P-values for each comparison are available in Source Data.