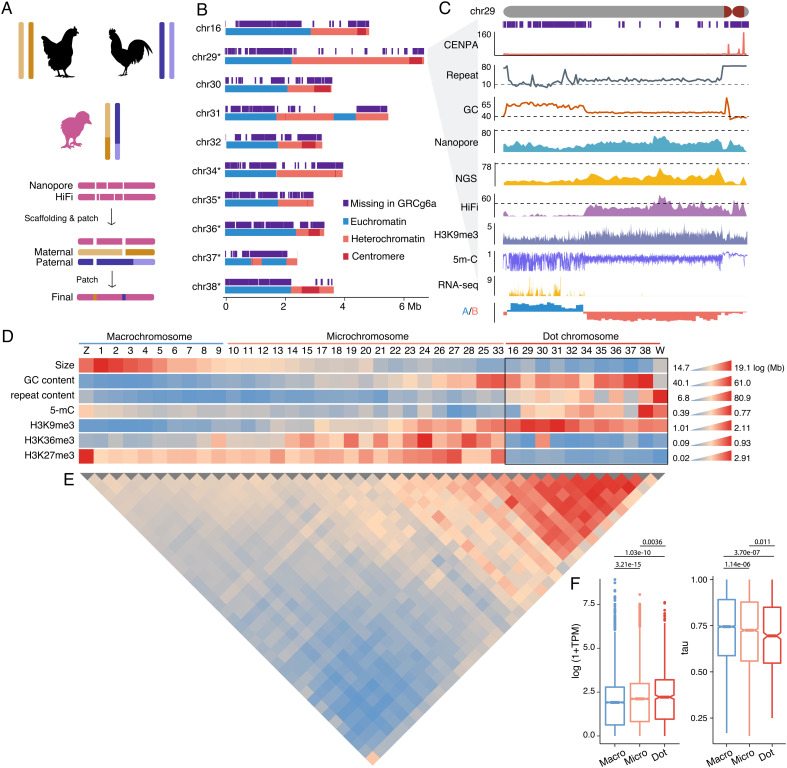
Fig. 1.
A complete chicken genome with 10 dot chromosomes. (A) A trio-based genome assembly pipeline. Rounded rectangles represent contigs. Paternal and maternal contigs were used to fill gaps in the primary contigs. (B) The dot chromosomes are in general composed of a euchromatic part and a heterochromatic part. The asterisks denote newly assembled chromosome models. (C) A zoom-in view for chr29, showing CENP-A and H3K9me3 binding, coverage of Nanopore ultralong, HiFi, NGS (BGISEQ-500, dashed lines indicate genomic average), gene expression (RNA-seq read counts in 1 kb windows), 5-mC levels, and A/B compartments. (D) The heatmap shows the chromosomal sizes (log-transformed), GC content, repeat content, chromosome-wide 5-mC levels, and ChIP/input ratios for H3K9me3, H3K36me3, and H3K27me3. (E) Interchromosomal interaction frequency measured using Hi-C data. (F) Dot chromosomes have a lower Tau value, i.e., lower level of tissue specificity but a higher expression level. P values were calculated using the Wilcoxon signed-rank tests.