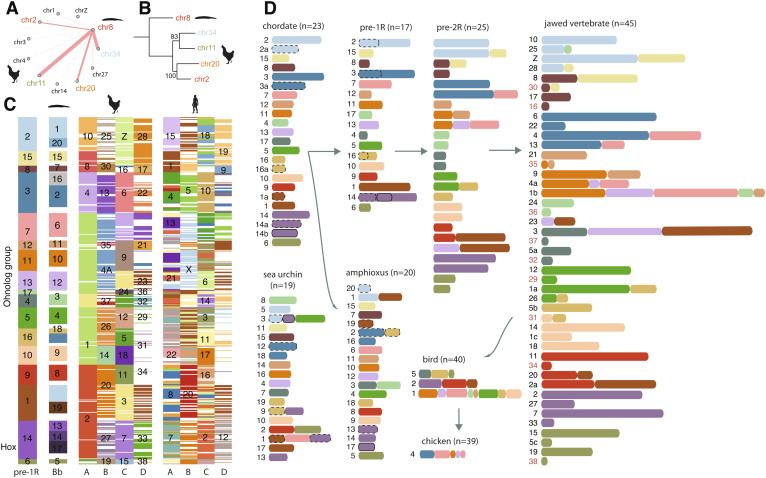
Fig. 3.
Chordate karyotype evolution. (A) Genes from amphioxus chromosome 8 are primarily homologous with those from four chicken chromosomes. The thickness of connecting lines indicates the relative abundance of homologous genes for chicken chromosomes. (B) Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of concatenated homologous genes from the homologous chromosomes in (A). Bootstrapping values are shown at the nodes. (C) 478 ohnolog groups that have at least three ohnologs in chicken. Each row represents one ohnolog group. The numbers indicate the chromosomes or ancestral linkage groups. White colors imply the absence of ohnologs. Chicken and human have up to four homologous chromosomes (A–D) for each amphioxus (Bb) chromosome. (D) The reconstructed evolutionary history of vertebrate chromosomes. The IDs of dot chromosomes are colored in red in the jawed vertebrate panel.