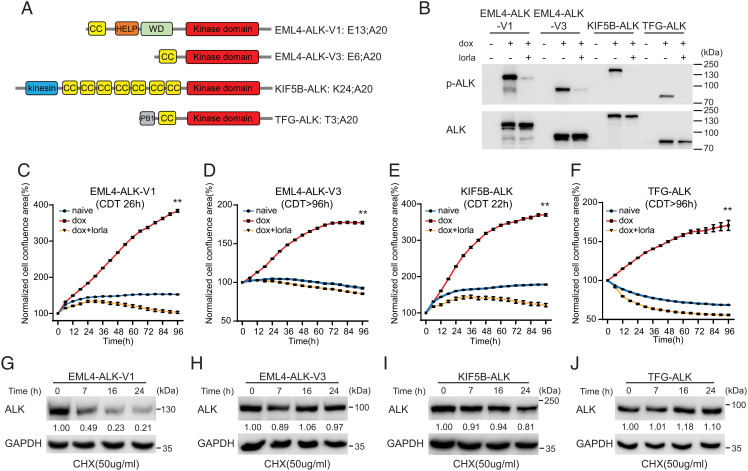
Fig. 1.
Characterization of NL20 cells expressing ALK NSCLC fusions. (A) Schematic representation of ALK fusion proteins investigated in this study. The breakpoint located at exon 20 in ALK is identical in all four ALK fusions. EML4-ALK-V1 (E13; A20) and V3 (E6; A20) harbor exons 1 to 13 and 1 to 6 of EML4, respectively; KIF5B-ALK (K24; A20) and TFG-ALK (T3; A20) contain exons 1 to 24 of KIF5B and exons 1 to 3 of TFG, respectively, fused to exon 20 of ALK. Protein domains are indicated as: coiled coil (CC, yellow), hydrophobic motif in EML proteins (HELP) (orange), tryptophan-aspartic acid repeat domain (WD) (green), ALK kinase domain (red), kinesin (blue), and PB1 (gray). (B) ALK fusions were induced in NL20-ALK cells with doxycycline (dox) in the presence or absence of lorlatinib (lorla, 30 nM), and lysates immunoblotted with pY1278-ALK and pan-ALK as indicated. PhosphoY1278-ALK (p-ALK) was employed as readout of ALK inhibition. (C–F) NL20-ALK cells were treated with DMSO (blue), doxycycline (red), or doxycycline plus lorlatinib 30 nM (orange). Cell confluence was monitored using an IncuCyte® Live Cell Analysis system. Data points represent mean ± SEM of normalized cell confluence conducted in triplicate. Cell doubling time of individual cell lines is indicated (**P < 0.01, two-tailed paired t test). One typical experiment of three independent experiments is shown. (G–J) NL20-ALK stable cell lines were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for 7, 16 and 24 h, and resulting lysates immunoblotted for ALK and Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Quantification of ALK fusion protein levels compared to GAPDH control is depicted below each lane (n = 3, a representative result is shown).