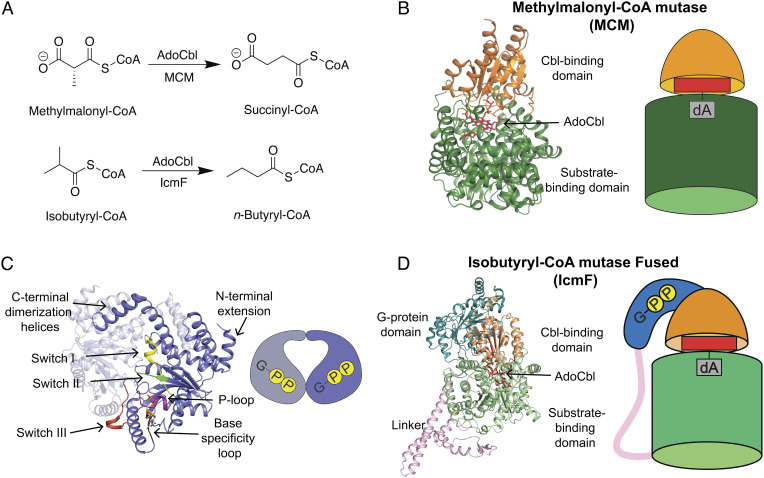
Fig. 1.
AdoCbl-dependent mutases require G-protein chaperones for maturation. (A) Reaction catalyzed by MCM (Top) and a reaction catalyzed by IcmF (Bottom). (B) The overall structure of the monomer of MCM from P. shermanii bound to AdoCbl (PDB 4REQ). The AdoCbl (red sticks) is bound at the interface of the Cbl-binding domain (light orange) and substrate-binding domain (green). The cartoon representation of MCM has the same coloring as the ribbon structure. (C) Signature motifs of the G3E P-loop GTPases shown on MeaB (slate) from M. extorquens bound to GDP (PDB 2QM7). The P-loop (purple, residues (res. 62 to 70) interacts with the phosphates of the nucleotide. The base specificity loop (brown, res. 200 to 207) interacts with the guanosine base. The switch I (yellow, res. 92 to 108), switch II (green, res. 154 to 158) and switch III (red orange, res. 177 to 188) function as switches signaling the GTP hydrolysis event. (D) The overall structure of one monomer of the dimeric IcmF from Cuprividius metallidurans bound to GDP and AdoCbl (PDB 4XC6) contains the Cbl-binding domain (light orange) and substrate-binding domain (light green) of the mutase on same polypeptide chain as the G-protein domain (teal) connected by a polypeptide linker (pink). AdoCbl (red sticks) is bound in the active site at the interface of the Cbl-binding and substrate-binding domains. The cartoon representation of IcmF has the same coloring as the ribbon structure.